Digital Tokens 101: What is a digital token?
Digital Tokens 101: What Does it All Mean?
The term ‘token’ can lead you to think about the plastic casino chips, or that thing used to swap to get a beer under a particular platform or within a particular market such as a festival.
Let’s explore the origin of this term ‘digital token’, and then have a look to the area of cryptocurrency tokens, differentiating between blockchain-native tokens like BTC on Bitcoin or even ETH on Ethereum, along with asset-backed tokens like IOUs on Ripple.
How Digital Tokens appeared
Chances are that we’ve all seen a digital token before, even though we didn’t realize it. Let’s think about when subscribing to an online service or newsletter.
After you enter an email address into a site to join a mailing list, you are often asked to look at your email and click a hyperlink. The link you get to confirm your subscription may look something like this:
https://www.website.com/confirm_email? token=4bdebebc-135b-4748-b7ab-25b31a285df8
In cases like this, the ‘token’ is that this series of characters that was delivered to you. This number or string of characters is unique, so the company who sent you the confirmation email will know it’s your email address if you click on it.
So, the site sent you a token, and you shipped it back, demonstrating you had control of the email address.
But the term ‘token’ is presently being utilized in a totally different manner to identify different items in the cryptocurrency world.
Cryptocurrency Tokens
Cryptocurrency tokens do not exist as a number like the one in the example above (they’d be simple to replicate ), but instead, they exist as entrances on a ledger (a blockchain). You have those ‘tokens’ since you’ve got a secret which allows you to make a new entrance on the ledger, re-assigning the possession to another person. You do not store tokens in your own pc, you save the keys that allow you to access or reassign the amount.
Those ‘tokens’ could be considered as electronic resources that you can have control of, and you may reassign control to somebody else.
“Cryptocurrency” can refer to both tokens and coins, but differences exist between the two labels.
We’ll cover two kinds of token:
- “intrinsic”, “native” or “built-in” tokens of blockchains
- “asset-backed” tokens issued on the blockchain by a third party onto a blockchain, which can be redeemed at a later time
1. Intrinsic tokens (also called ‘native or ‘built-in’ tokens)
Intrinsic tokens are conceived for their usefulness.
Here are some famous examples of intrinsic tokens are:
- BTC (Bitcoin blockchain)
- XRP (Ripple network)
- NXT (NXT platform)
- ETH (Ethereum)
Check out the top 100 cryptocurrency tokens, and the entire list on Coin Market Cap.
All these ‘coins’ or ‘digital tokens’ stand at the core of their projects and blockchain. Without them, the blockchain wouldn’t work. It’s not rare to find digital tokens as part of a reward system, which encourages users to create blocks by validating transactions on the blockchain. Each blockchain has its own digital tokens system, although some can look alike.
How are intrinsic tokens created?
These tokens are created by computers and are not backed up by anything. It’s like writing down on a piece of paper “I have 1 billion coins”.
In reality, if you did this, then kept a fantastic record of those friends you gave them to, and in the event that you could record forward trades as your buddies gave them to other friends, you’d do pretty much exactly what these digital ledgers do.
Let’s take the most famous digital tokens for instance:
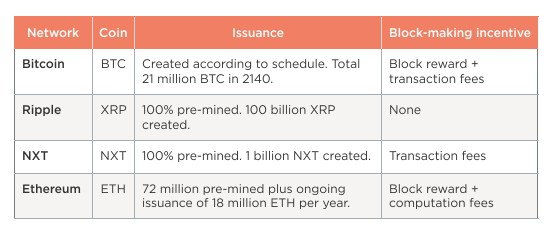
- Bitcoin, BTC
Bitcoins are ‘mined’ according to a schedule. The recently created coins are made to reward to the block-maker. The entire amount of bitcoins increases with time. They can be then traded.
- Ripple, XRP
The digital tokens XRP, were ‘pre-mined’ (created all the beginning) and shared among key participants. Each trade has a small XRP fee. These XRPs are destroyed over time. The entire amount of XRPs circulating goes down with time.
- NXT, NXT
The NXT tokens were pre-mined. Each trade on the NXT system includes a commission in NXT. The fee goes into the block-maker (in NXT that is known as a ‘forger’ as opposed to a ‘miner’). The entire amount of NXT stays constant with time.
- Ethereum, ETH (‘Ether’)
Ethereum has been pre-mined. Transactions and smart contracts require an ETH fee to be created and to operate, and the block-maker is rewarded with ETH. The block-maker also receives a block reward.
What is the purpose of intrinsic digital tokens?
The primary purposes of intrinsic digital tokens appear to be:
- Block validation incentives (‘miner rewards’)
- Transaction spam avoidance (if all trades cost a token, it restricts the capacity to create spam transaction and jam the network)
Even though these coins have worth (you can purchase and sell some of them on a cryptocurrency exchange for some other cryptocurrencies or fiat), they are not supposed to represent anything. They just exist as a digital token.
2. Asset-backed tokens
If we take a look at the history of money, we can observe an antique practice people had. In the old times, you could deposit gold at your goldsmith’s shop, and get a receipt or “I Owe You” (IOU) note from them. These notes could be moved from person to person, and anyone holding these notes could go back to the goldsmith and get into the possession of the actual gold.
Asset-backed tokens would be the electronic equivalent. They’re claims within an underlying asset (such as the golden), that you have to maintain from a particular issuer (the goldsmith). The trades are listed on the blockchains, as tokens become passed between individuals, and also to maintain the underlying asset, you ship your token into the issuer, and the issuer sends you that the underlying asset.
Asset-backed tokens are claims on an underlying asset, by a particular issuer.
Popular assets for all these schemes are currencies (USD, EUR, etc) and precious metals (Cryptocurrencies seem to attract the same crowd as silver and gold). People monitoring these assets on ledgers by producing a digital token to represents each of them.
How do asset-backed tokens work?
Let us take the case of Coins-R-Us, a false Bitcoin exchange, issuing Euro-backed digital tokens.
You send fiat money to Coins-R-Us by logging into your internet banking. It’s like a normal bank payment you sent Eur to the Coins-R-Us’ bank accounts. Let’s say you sent 100 Eur. Then you log into your account and see 100 electronic asset-backed tokens known as Coins-R-Us-EUR.
The production of the tokens is listed on a blockchain. This could be on the Bitcoin Blockchain, or as a resource on Ripple or NXT, or even a smart contract on Ethereum. Now you can send these digital tokens to your friends (possibly in return for some thing or as a present), and also the tokens continue to be monitored on the exact same blockchain.
At some point, one of your friends will want to exchange this asset-backed token to get something real. He would have to go back to Coins-R-Us, set up an account on their platform, tell them his bank account number, and send them the Coins-R-Us-EUR he got out of you. They would then sent him Eur to his bank account from their bank account.


What are Cryptocurrencies?
What is the definition of cryptocurrency?
A cryptocurrency is a virtual or digital currency which is encrypted (secured) using cryptography. Cryptography refers to the usage of encryption methods to secure and check the transport of trades. Bitcoin represents the very first decentralized cryptocurrency, which can be powered with a general public ledger that lists and validates all trades chronologically, known as the blockchain.
A Cryptocurrency is a math-based, decentralized digital money that’s protected by cryptography
Cryptocurrency is a short expression for “cryptographic” money. Cryptocurrency integrates the principles of cryptography to execute a distributed, decentralized, protected information market.
Cryptocurrency is a kind of “virtual money” compared to fiat money that’s used more commonly, like the dollar or the euro. Virtual currencies are supposed to be utilized as money; they are mainly meant to be utilized as a medium of trade. Though some persons speculate about the value of one currency versus different money, the aim of these currencies is to be used as a medium of trade rather than as an investment.
In 2015, the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) from the United States, declared that “Bitcoin and other virtual currencies are encompassed in the definition and properly defined as commodities.” However, because virtual currencies aren’t securities, they aren’t regulated by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
Briefly, this is how a blockchain functions:
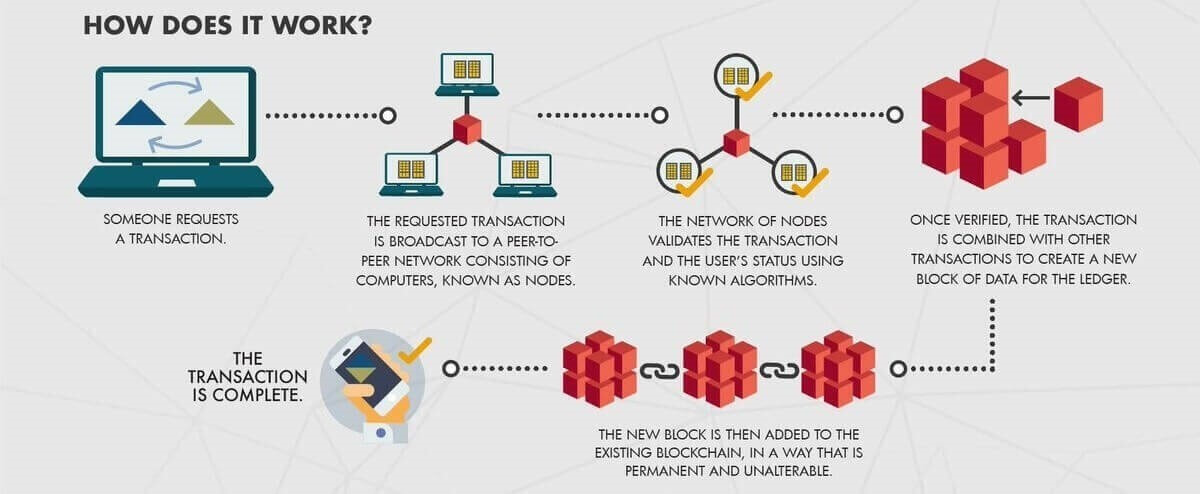
(Source: The Bernie Group)
Cryptocurrencies have been around before Bitcoin was created, but its creation marks a significant milestone in the domain of digital currencies, mainly because of its decentralized blockchain and user adoption.
The development of Bitcoin precipitated the growth of a verdant and much more varied ecosystem of different coins and tokens, which are frequently regarded as cryptocurrencies generally, even if a lot of them don’t fall under the definition of “money”.
Digital tokens vs Cryptocurrency
The cryptocurrency discussion is always changing, and it can be confusing and mysterious, especially when we start talking about digital tokens.
Ever noticed tokens being known as coins, and coins as slogans? Or what about cryptocurrency together with tags like “safety” and “usefulness”?
It’s important to understand the concept of cryptocurrency because digital tokens do fall under it.
Cryptocurrency is encrypted and decentralized with cryptography and is a form of digital money made and saved on the blockchain. There are many cryptocurrencies, all of which are utilized to control the production of financial units and also to check the transfer of capital. The expression “cryptocurrency” identifies all coins and tokens.
Therefore, what’s the difference between a digital coin and a digital token?
Coins (Bitcoin and altcoins) have their own independent blockchain and their objective is to replace cash and to be used as a unit of account, store of value and medium of transfer.
Tokens, on the other hand, are usually an addition to a blockchain and reflect an asset or a utility. Digital tokens belong to a platform (e.g. the Ethereum network), to exist and function, and are created when a crypto project launches an Initial Coin Offering (ICO). Tokens, also known as crypto-tokens and digital tokens, are often given to early investors in exchange for cryptocurrencies such as Ether, Bitcoin, or even some other Altcoins, and can also be used as a kind of payment for utilizing a platform, or app.
Now, how do you tell exactly what token does what? There is a number token and they all exist independently. However, the main types of tokens are security tokens and utility tokens.
In the crypto space, people refer to digital tokens as crypto tokens.
Think of digital tokens the same as you would think of the tokens that we utilized in actual life actions. The most important intention of the tokens would be to provide clients with an equivalent priority for maintaining an item or something that the tokens belong to.
For example, in banking, they utilize tokens to facilitate the customers’ access to their account.
Digital tokens work in a similar manner, but they’re primarily utilized at the idea of ICO.
Coins vs Tokens: Categorization of Cryptocurrencies
It’s essential to be aware that all coins or tokens are considered as cryptocurrencies, even though the majority of the coins don’t be a currency or medium of exchange.
The expression cryptocurrency is a misnomer because money technically signifies a unit of account, a store of value and a medium of trade.
These features are inherent inside Bitcoin, also since the cryptocurrency area was kick-started by Bitcoin’s production, some other coins conceived following Bitcoin is normally believed to be a cryptocurrency, although most don’t meet the aforementioned qualities of genuine currency.
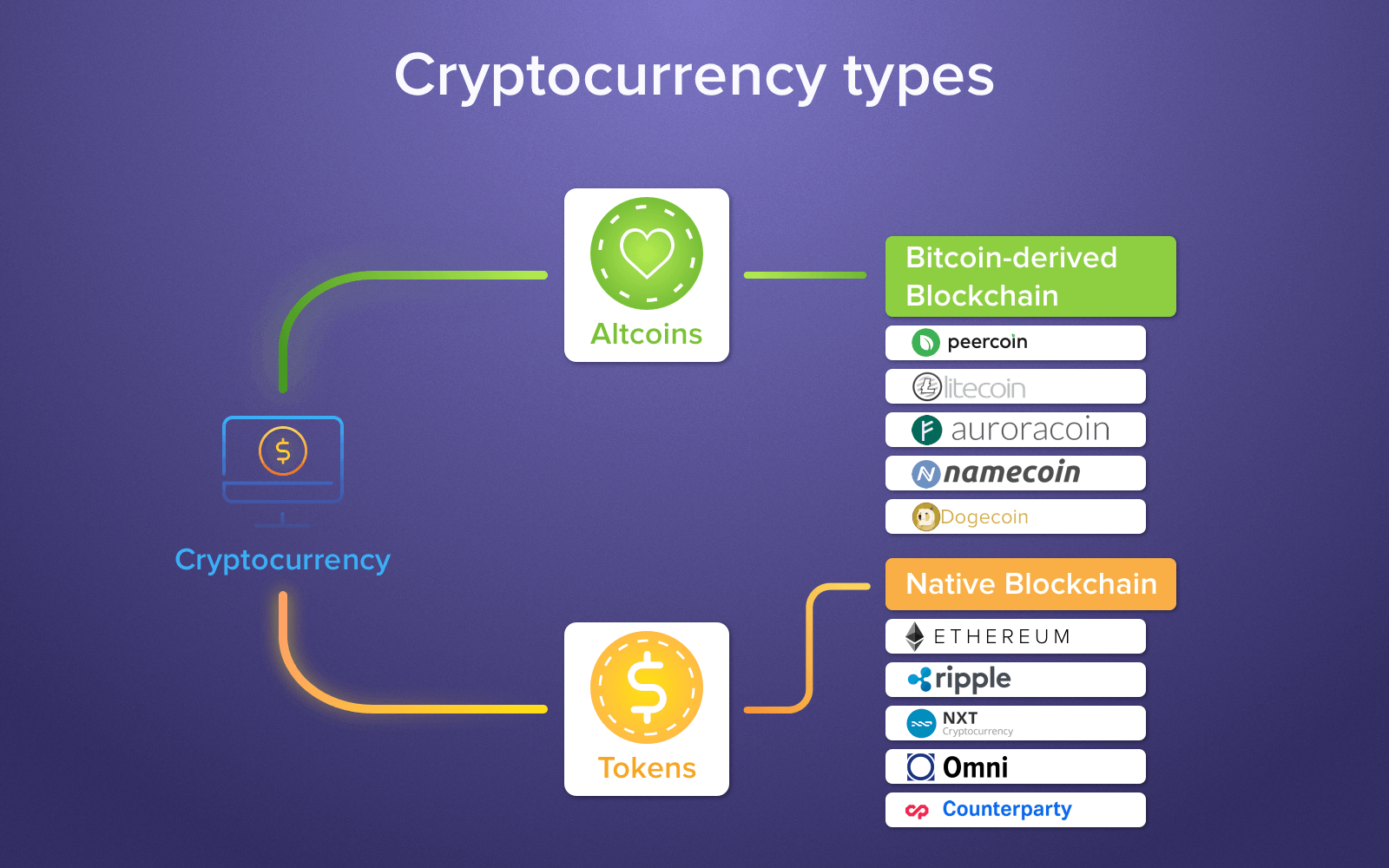
The most frequent categorization of all cryptocurrencies are:
- Choice Cryptocurrency Coins (Altcoins)
- Tokens