Is blockchain going to Space?
Blockchain in FinTech
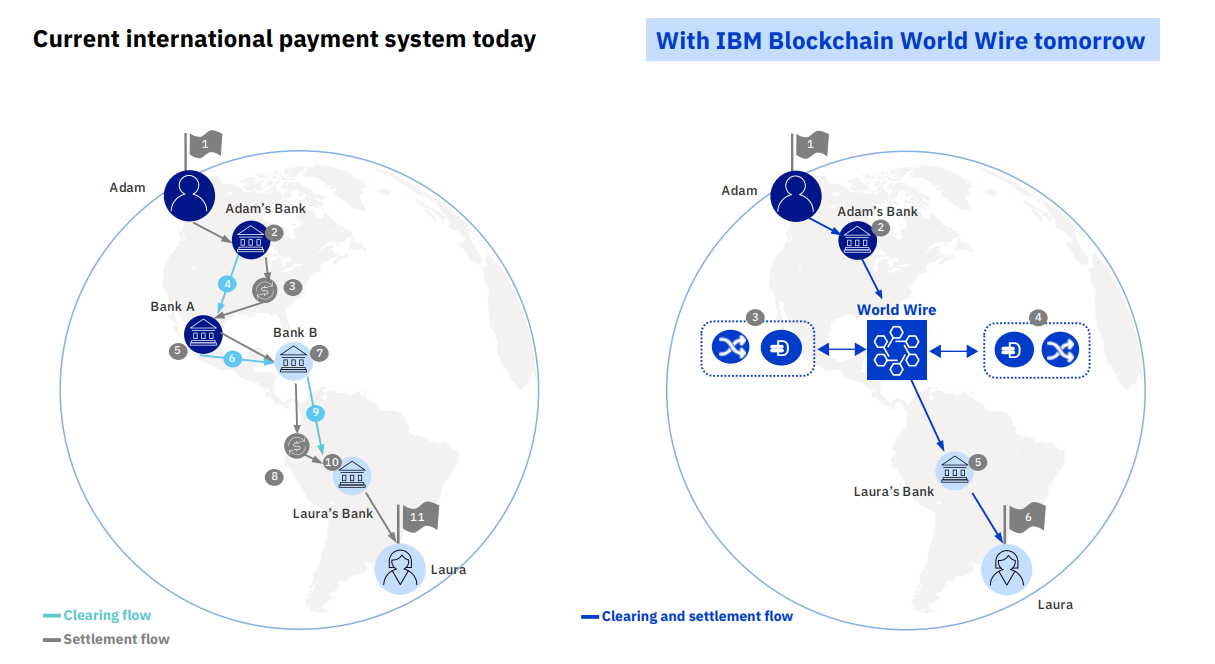
With its roots in fintech, blockchain has helped empower the cryptocurrency trend that started with Bitcoin. These days, the entire world is moving toward electronic possession of cash. The main reason is the decentralized ledger that blockchain uses, the blockchain.
Back in August 2017, a mistake by Google temporarily caused almost half of Japan to be denied access to the internet. While connectivity has been restored over the hour, users underwent slow link rates, which influenced industries like finance, where online trading has been stopped.
Within this scenario, dispersing the bitcoin blockchain through satellite could have assured the blockchain stayed in sync with the rest of the planet and so, unaffected by net outages.
Blockchain technology today touches virtually every business, by protecting medical records and individual privacy, to monitoring food security and medicine supply chain compliance, to supporting art credibility, to validating petroleum and gas trades as well as property ownership internationally.
Within the international space business, new and existing space innovators attempt to capitalize on blockchain’s assurance from the race into Low-Earth orbit (LEO), producing new opportunities for cooperation, new satellite-as-a-service business models, and new techniques to deal with the space distribution chain as well as how to construct payloads.
“There are huge opportunities for blockchain in satellite networks,” says Helena Correia Mendonça, chief consultant in the aerospace and ICT branches of a Portuguese law company, Vieira de Almeida (VdA), in which she has educated African American and European customers on space issues. She believes the embracing blockchain in the space industry was the natural step in blockchain’s expansion.
Enhancing the Satellite Value Chain
Mendonça states blockchain in satellites generates transparency, confidence, and efficacy in the satellite worth series.
For example, in logistics, utilizing smart contracts for starting and operating satellites, obtaining transparent data for insurance purposes, and exercising governmental functions (for example resorting to blockchain from the licensing procedure for establishing a satellite and also in tracking space surgeries).
It’s also beneficial in regards to the supply of blockchain data via satellite and even in turning tanks to “smart emancipated devices” through utilizing smart contracts.
Satellites may also be significant sources of distance information for upgrading blocks and confirming the integrity and source of data. And will drive smart contracts and logistics software while being really beneficial to the insurance market.
In a developing area such as Africa, it might also lead has contributed to more fiscal inclusion due to satellites’ ability to connect those otherwise excluded.
“One of the issues many of these countries have is determining the ownership and registering land, as well as identity … We know developing countries are using their government’s blockchain for this purpose,” says Mendonça. “If you get blockchain in satellites, you also get the benefit of blockchain without the need for these huge investments in ground networks.”
Blockchain can consequently become truly global using satellites.
Deep space applications like space mining may also leverage blockchain to help monitor and manage tools, states Mendonça.
Brian Rider, CTO for Seattle-based LeoStella, that is revolutionizing constellation structure of smallsats, sees two programs for blockchain in distance.
The first is supplying a worldwide distribution system that’s persistent and sovereignty agnostic. The second one is utilizing the blockchain to deliver advantage computing processing to distance.
“I really think it could become the core of how satellite activity and tasking are secured [in the future],” he says. “The thing that keeps me up at night is not hackers breaking into data that is being transacted across a satellite, but hackers taking control of satellites. Blockchain is a key aspect of how we will secure our constellations in addition to using blockchain to support commercial transactions.”
Deep space applications like space mining may also leverage blockchain to help monitor and manage tools, states Mendonça.
Dennis Gatens, a 30-year veteran of satellite, cloud and telecom solutions, currently serving as Chief Commercial Officer (CCO) for Cloud Constellation, agrees, noting that assignments to the moon and especially Mars will need crews to make conclusions “inside the human loop” due to transmission time delays involving crews close or around Mars and tools back on Earth.
Edge computing, empowered by blockchain and AI, will perform crucial roles. “Eventually, deep space will become part of the national security strategy, and blockchain will play a valuable role in making sure that data is secure and not compromised,” he says.
Enabling Cloud Services in Space
Cloud Constellation and IBM’s Space Tech group hope to leverage both AI and blockchain as they work to enable a cloud transformation in space.
The two companies, in a current co-authored white paper, compared the importance of blockchain in distance to the first Industrial Revolution.
Gatens states Cloud Constellation intends to provide global connectivity directly into the enterprise and protected data storage in orbit, using a roadmap to data and advantage computing from IBM, as a part of its SpaceBelt Data Security as a Service (DSaaS) portfolio.
Blockchain over satellite gets rid of the dependence on terrestrial infrastructure to the movement, memory, or computation of information and that, based on Gatens, eliminates a substantial vulnerability for information breach or compromise of information.
“Blockchain gives you the ability to have a chain of custody associated with data, whether the data is at rest or in motion; from end-user to end user, satellite to satellite, moving in and out of storage on our satellites, or you are combining it with artificial intelligence to look for anomalous transactions or attempts at anomalous transactions.”
Tracking the Satellite Supply Chain
Naeem Altaf, IBM’s Distinguished Engineer and CTO for SpaceTech, sees great opportunities for SpaceBelt and IBM’s blockchain service to monitor and confirm the transport and trust of providers throughout each stage of the procurement, construction, launching and testing of a satellite.
“Today, we use terrestrial networks to talk to data centers,” he says. “In the future, Cloud Constellation will have a sort of data center in orbit where companies can upload their data and bypass the terrestrial network.”
Authorities and fiscal applications will be to embrace the space blockchain, Altaf states, though other businesses will not be far behind. Altaf says any business with sensitive information along with a great deal of remote websites which will need to acquire information from various sources may use space blockchain.
Another place is that the production of satellites out of procurement to the launching website: blockchain could monitor a satellite’s motion, sharing information with all providers, and may apply rules like any modifications made to the satellite demand the validity of the group.
Cloud Constellation chose Seattle-based LeoStella to construct its 10-satellite LEO system. Nine will probably be busy and the last one will work as a hot spare and will have a first data storage capacity of 1.6 petabytes for clients on orbit.
“We selected LeoStella because they aligned with our vision and have the ability to manufacture the kind of satellite we need,” says Gatens
Two optical rings will interconnect the whole constellation to guarantee redundancy and self-healing for high accessibility. The SpaceBelt system will communicate with protected SpaceBelt access points situated at business clients’ places via connectivity with present Geosynchronous Orbit (GEO) satellite services.
“We are about two-and-a-half years away from first service availability and we hope to do some early customer evaluations in the service in fourth quarter of 2021,” says Gatens.
Even though Cloud Constellation has recently started to talk about blockchain, two additional companies have made remarkable inroads: Blockstream and SpaceChain.
Enhancing the World’s First Blockchain-enabled Public Satellite Service
“We see satellite technology as very useful to augment and reinforce exiting blockchain applications,” states Chris Cook, CTO, Blockstream, a blockchain and fiscal cryptography firm, and also the first to disperse bitcoin blockchain via satellite.
Bitcoin now has a market cap of $183 billion and the general cryptocurrency market cap is $273 billion, even though Cook quotes the total market size to become substantially bigger if one counts all of the ancillary businesses in the business.
Blockstream jumped to the space industry with Blockstream Satellite, just two years ago. This is the world’s earliest public satellite service which permits everyone to operate and keep bitcoin nodes, without the limitations of conventional network connectivity.
The service, provided from five transponders on four GEO communication satellites, is absolutely free to anybody as soon as they buy about $100 in parts, including a tiny 45-inch antenna. Cook states Blockstream does not have any clue how many consumers are utilizing the system since the service and network are made to safeguard the anonymity of consumers.
“When we launched in 2017, we had two-thirds of the world covered: North America, South America, Europe and Africa,” says Cook, adding that Asia Pacific from Australia to Japan, China, and part of India was added a year later.
“Our forthcoming release, which is outside in the Fourth Quarter (Q4), is a large improvement to the ceremony at which we’re further increasing our policy and accessibility options around the globe and are raising our bandwidth with more interesting programs,” says Cook, signaling the bandwidth has improved by a factor of five and also the Asia/Pacific area, which now utilizes C-band connectivity, will probably be incorporating Ku-band for a portion of the area.
“While our core satellite network is designed to distribute the bitcoin blockchain, we’ve also enabled service where anybody can send any data they want via our satellite network and then pay for it in bitcoin,” he adds.
Leveraging Open Source Satellites for Constellation Collaboration
Singapore startup SpaceChain, a partner of Cloud Constellation, is constructing an open-source satellite community that incorporates blockchain. The organization’s CEO and creator Zee Zheng considers that these technologies will allow a new age of seamless international cooperation.
The business introduced two blockchain-enabled satellite payloads into orbit over SpaceChain’s initial year of operation and three more are planned in the following 18 weeks.
“Our satellite payloads are the only blockchain-enabled satellite payloads in the world right now,” says Zheng. “We have witnessed how the smartphone industry has evolved and we see this trend for software-defined satellites. If they offer a secure development environment with an open-source platform, there is great potential.”
SpaceChain now supplies a satellite crypto wallet over SpaceChain’s personal network, enabling transactions without using the world wide web.
Zheng says new area companies are wanting to utilize the blockchain to forge partnerships with different businesses. They would like to explore constructing a joint constellation collectively by sharing with an open-source platform.
“We want to have multiple startups launch satellites to form a constellation with a shared protocol,” says Zheng. “It will no longer be one company launching 70 to form the constellation; it can be five companies and each of them launches 10 to 15, to form the constellation together. We believe blockchain creates many new opportunities to partner — which is one thing the industry is lacking.”
Zheng notes that SpaceChain would like to use open-source distributed technology to earn more application uses instances and, at precisely the exact same time, more decentralized networks to the space market.
Identifying Hurdles to Widespread Blockchain Space Adoption
There are some issues that need to be overcome before blockchain programs become mainstream.
IBM’s Altaf believes the largest problems is that blockchain is a process-based alternative which needs organizations to agree to operate a specific way, something which could possibly be challenging in the satellite market where businesses are often reluctant to share info.
“Big players like Amazon and Walmart can force their suppliers to adhere to their blockchain network because they are their biggest customer,” he says. Not true for the satellite industry.
Another issue concerns the hardware differences between terrestrial and distance networks. The distance blockchain demands radiation-hardened hardware.
“Most of this architecture is proprietary — we have to do a lot more work to get Intel or ARM (Advanced RISC Machines) processors, currently used on your phones or to run your computer, hardened enough to work in space.”
Irrespective of the operational versions, all space blockchain advocates agree on something: the potential for blockchain software in distance is unstoppable and will result in unprecedented new service capacities.
Blockchain, LEO Market Spark More Nimble Satellite-Manufacturing Models
Keeping pace with the explosion in LEO constellations and satellite versions which are leveraging technologies such as AI and blockchain demand new revolutionary approaches not just in orbit but using satellite payload layout, based on Brian Rider, CTO of LeoStella.
Formed as a joint venture between Thales Alenia Space and Spaceflight Industries, that delivers the Dark Sky geospatial intelligence assistance, LeoStella looked in the exploding LEO marketplace and recognized that it had a much better, nimbler version for constructing satellites which could benefit from inventions like blockchain and AI.
“We don’t think of ourselves as a traditional small satellite market … but as a forward-thinking, constellation and space infrastructure provider,” says Rider.
The business helps commercial businesses such as Cloud Constellation that need to make value-added cloud solutions from area infrastructure ascertain the best means to do it in a design standpoint.
It has the ability to create around 40 satellites per year within their Seattle mill, which follows procedures and manufacturing methodologies utilized in the automotive sector. In accordance with Rider, LeoStella’s manager of programs formerly led the distribution chain for Tesla’s semi-truck jobs.
“We have the ability to take satellites or long-lead components off the production line and quickly repurpose them to create a first-to-market advantage,” he says.
The business also provides complete transparency to its own manufacturing line, together with LeoStella and clients together making decisions regarding risk and schedule.
“We provide opportunities to bring in new technology — if a new communications or camera system comes on the market, we can integrate those into production where satellites are actively being produced,” he says.