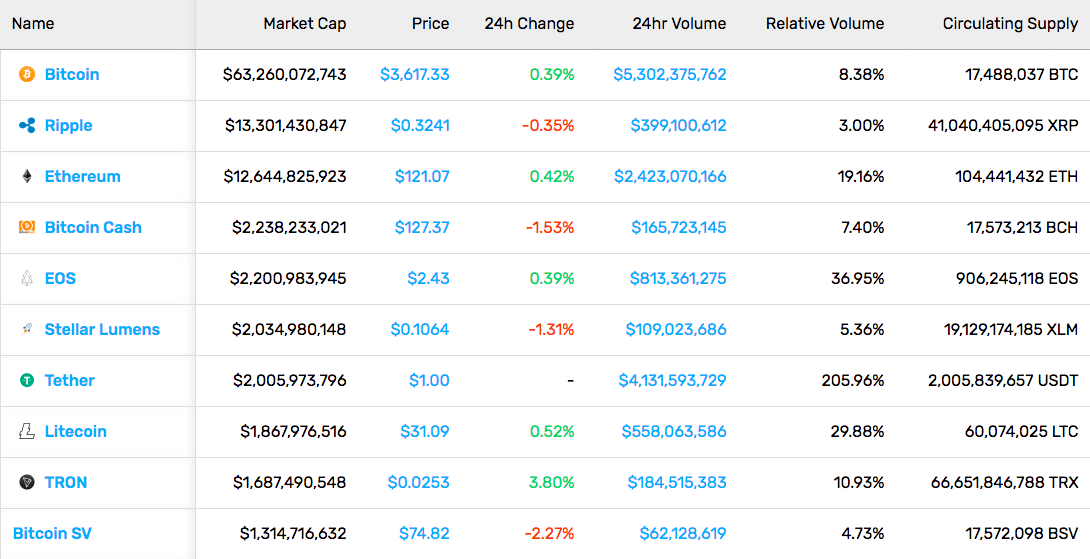
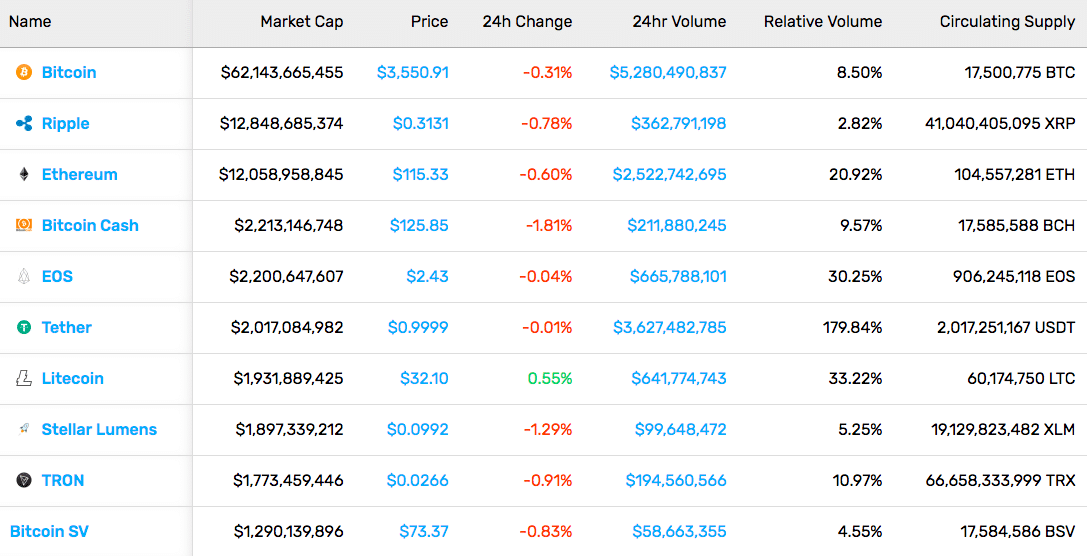
The cryptocurrency market has become crowded, with new cryptocurrencies coming out daily, while old ones disappear faster than ever. Let’s check out the top 20 cryptocurrencies, as they appear on coinmarketcap.com
1. Bitcoin (BTC)
Bitcoin is the king of the crypto world. To most, it’s interchangeable with”cryptocurrency.” Its objective is to extend a peer-to-peer digital model of money to permit payments to be routed online with no necessity for a third party (like Mastercard).
The rapid increase in Bitcoin’s cost has caused an explosion of fresh Bitcoin investors. With the massive growth in interest has come an increase in retailers accepting Bitcoin as a valid type of payment. Bitcoin is quickly moving towards its objective of being a currency accepted globally.
Read more on What is Bitcoin?
2. Ethereum (ETH)
Ethereum is the revolutionary platform that brought the concept of “smart contracts” into the blockchain. First released in July 2015 by then 21-year-old Vitalik Buterin, Ethereum has quickly risen from obscurity into cryptocurrency celebrity status.
Buterin has a complete team of developers working supporting him to further develop the Ethereum platform.
Ethereum has the power to process transactions quickly and cheaply over the blockchain very similar to Bitcoin but also has the ability to run wise contracts. Think about automated processes which can perform just about anything.
Read more on What is Ethereum?
3. Ripple (XRP)
Ripple aims to improve the speed of monetary transactions, specifically international banking transactions.
Anybody who has ever sent cash globally knows that today it now takes anywhere from 3-5 business days to get a transaction to clear. It is quicker to draw money, get on a plane, and fly to a destination than it would be to ship it! Transaction fees are generally around 6%, but it can vary based upon the financial institution.
Ripple’s objective is to earn these trades fast (it only takes around 4 minutes for a trade to clear) and economical.
The Ripple team now comprises over 150 people, making it among the largest from the cryptocurrency world. They’re headed by CEO Brad Garlinghouse, with an impressive resume which includes high rankings in different organizations such as Yahoo and Hightail.
Read more on What is Ripple?
4. Bitcoin Cash (BCH)
Bitcoin Cash was created on August 1, 2017, after a “hard fork” of the Bitcoin blockchain. For a long time, a debate has been raging in the Bitcoin community on whether to increase the block size in the hope of relieving some of the community bottleneck which has plagued Bitcoin due to its increased popularity.
Because no agreement could be reached, the original Bitcoin blockchain was forked, leaving the Bitcoin series untouched and in effect creating a brand new blockchain which would allow developers to modify a number of Bitcoin’s first programmed features.
Generally, the debate for Bitcoin Cash is that by allowing the block size to increase, more transactions can be processed in precisely the same amount of time. Those opposed to Bitcoin Cash assert that increasing the block size will increase the bandwidth and storage requirement, and in effect will cost out normal users. This could cause increased centralization, the exact matter Bitcoin set out to avoid.
Bitcoin Cash doesn’t have a single development group like Bitcoin. There are currently multiple separate teams of developers.
Read more on What is Bitcoin Cash?
5. EOS (EOS)
Billed as a possible “Ethereum Killer,” EOS suggests improvements which can challenge Ethereum because of the prominent smart contract platform. 1 main issue EOS appears to enhance is the scalability issues that has plagued the Ethereum platform during times of high trade volume, specifically during popular ICOs.
A possibly more profound gap EOS has, compared to Ethereum, is the way in which you use the EOS network. With Ethereum, every single time you make modifications or interact with the network, you have to pay a fee. Together with EOS, the creator of the DAPP (decentralized program ) can foot the bill, while the consumer pays nothing. And if you consider it, this is reasonable. Would you need to pay each time you post something on social media? No, certainly not!
Along with this, EOS includes a few other technical advantages over Ethereum such as delegated proof-of-stake and other routine changes. Just know that EOS has some serious power under the hood to back up the claim of “Ethereum Killer.”
EOS was created by Dan Larrimer who’s no stranger to blockchain or even start-ups. He has been the driving force behind numerous successful projects in the past, for example, BitShares, Graphene and Steem.
Read more on What is EOS?
6. Stellar Lumens (XLM)
In brief, Stellar Lumens attempts to use blockchain to create very fast international payments with little fees. The network can handle tens of thousands of transactions a second with only a 3-5 second confirmation time.
As you may know, Bitcoin can sometimes take 10-15 minutes to get a trade to affirm, can only deal with a few transactions a second and, in turn, has very high transaction fees.
This sounds much like Ripple! Stellar Lumens was founded on the Ripple protocol and is attempting to do similar things. Some of Stellar Lumens’ main uses will be to making small daily payments (micropayments), sending money internationally, and mobile payments.
Stellar Lumens is focusing on the developing world also, more specifically, the dollar industry of researchers who send money back to their own family in impoverished nations.
The Stellar Lumens group is led by Jed McCaleb, who’s worked in a number of successful startups in the past such as eDonkey, Overnet, Ripple, along with the notorious Mt. Gox.
Read more on What is Stellar?
7. Litecoin (LTC)
Very similar to Bitcoin, Litecoin is a peer-to-peer transaction platform designed to be utilized as an electronic currency. Because of some noteworthy technical advancements, Litecoin is able to handle more transactions at lower prices. Litecoin was made to process the tiny transactions we create daily.
Litecoin is referred to “digital silver” while Bitcoin is known as “digital gold” This is because traditionally silver has been used for little daily trades while gold was used as a store of wealth and was not used in regular life.
The Litecoin blockchain is a fork from the Bitcoin series. It was originally established in 2011 when its founder, Charlie Lee, was still working for Google. Well-known as a cryptocurrency expert, Charlie Lee is backed by a solid development team who seem to be achieving what they set out to perform. They have recently attained a very notable accomplishment using the first successful nuclear swap.
Read more on What is Litecoin?
8. Tether (UDST)
Tether is a cryptocurrency token issued on the Bitcoin blockchain. Each Tether coin is allegedly backed by one US Dollar. The target is to facilitate transactions with a rate fixed to the USD.
Amongst other things, Tether looks to resolve a number of the legal issues which could arise when trading cryptocurrencies also it aims to protect people from market volatility.
Tether has faced controversy concerning their business model, and some believe it a scam.
Read more on What is Tether?
9. Cardano (ADA)
Cardano is a smart contract-focused blockchain. It was originally released under the title Input Output Hong Kong by Charles Hoskinson and Jeremy Wood, Some of the first team members of Ethereum, and afterwards rebranded into Cardano.
Cardano is hoping to correct some of the largest issues the cryptocurrency world which have been causing continuing problems for many years like scalability issues and democratized voting.
They have the potential to challenge Ethereum’s dominance in the smart contract world. Cardano is growing their own programing language similar to Ethereum; however, they’re focusing heavily on being interoperable involving other cryptocurrencies.
While some cryptocurrencies are all bite but no bark, Cardano is quite the opposite. They are quietly focusing on strong software which will be wholly open-source.
Cardano’s team contains some of the greatest minds in the market, and they seek to create a solid foundation which others may build upon for many years to come.
Read more on What is Cardano?
10. IOTA (MIOTA)
IOTA has seen lots of the problems Bitcoin and Ethereum have with the PoW (Proof-of-Work) and PoI (Proof-of-Importance) versions and seems to improve them with their revolutionary transaction validation network only called “Tangle.”
When issuing a transaction in IOTA, you affirm two previous trades. This means that you no longer outsource validation to miners which necessitates wasteful amounts of computing power and also normally a large bet of coins. These necessary resources are, in effect, centralizing the monies which many believe were created to be decentralized in the first place.
With IOTA, the more energetic that a ledger is, the more validation there’s. In other words, the more individuals using it, the quicker it gets. You do not have to subsidize miners, so there are no charges on transactions. That’s right: zero.
The IOTA team was actively growing blockchain technology since 2011, and established the IOTA foundation and company in 2016. Since its emergence, the group has been continuously growing, bringing exceptional talent from around the world.
Read more on What is IOTA?
11. TRON (TRX)
As stated in TRON’s whitepaper, “TRON is an attempt to cure the internet.” The TRON founders think that the world wide web has deviated from its initial intention of enabling people to freely create articles and article as they please; alternatively, the world wide web was taken over by huge corporations like Amazon, Google, Alibaba and many others.
TRON is attempting to take the internet back from these types of companies by building a free content entertainment program. This will make it possible for users to openly store, publish and own information, giving them the capability to determine where and how to talk.
The project is directed by creator Justin Sun, that has been listed on the Forbes 30 under 30 list double (in 2015 and 2017). Additionally, Sun is a protégé of Jack Ma, founder of Alibaba Group, China’s former Ripple representative along with the creator of Peiwo APP.
Sun has built a powerful team with heavy hitters including Binshen Tang (creator of Clash of King), Wei Dai (founder of ofo, the biggest shared bicycles provider in China), also Chaoyong Wang (founder of ChinaEquity Group). Sun has also secured the aid of a few notable angel investors such as Xue Manzi.
Read more on What is TRON?
12. Monero (XMR)
Monero is a digital currency made to be used as a totally anonymous payment system.
A common misconception with Bitcoin is the fact that it is completely anonymous. In reality, all payments processed around the Bitcoin network are recorded on a public ledger (blockchain), so Bitcoin is actually only partially anonymous or “pseudonymous.”
This usually means that you can, in theory, trace back every transaction a coin has been involved with out of its creation. Though users are not able to inherently connect the people key on the blockchain together with the private keys used to store the coins themselves, there’ll always exist a correlation between the two.
Monero has solved this issue by implementing cryptonic hashing of receiving addresses, therefore dividing the coin out of the address it is going to. This can be hugely valuable for anybody wanting to hide their buys.
The Monero development group consists of 7 core developers, only two of which are publicly known. There have been over 200 additional contributors to the project and software updates are implemented every six months or so.
Read more about What is Monero?
13. Dash (DASH)
Dash (that comes from “digital cash”) intends to be the most user-friendly and scalable cryptocurrency on the planet. It has the capacity to send money instantly confirmed by “double-send-proof” safety with the extra functionality of erasable trade history and the capacity to send transactions anonymously.
Much like Bitcoin, Dash is supposed to be utilized as electronic money but has some added values such as much faster transaction times and reduced fees. For a slightly higher fee, Dash has the additional role of “minute send” which permits transactions to be verified almost immediately. This is only one of the principal selling points of Dash because most believe this attribute would allow it to be utilised in physical establishments.
The Dash development team is made up of over 50 members and is directed by former financial services specialist Evan Duffield.
Read more on What is Dash?
14. Ethereum Classic (ETC)
Ethereum Classic came after a hard fork of Ethereum in 2016. The fork has been a consequence of the infamous DOA hack where around 50 million bucks worth of Ethereum was stolen due to what was considered an oversight in the code.
The blockchain was forked so as to recover the losses from this attack, but a small portion of the community did not want to go back and alter the initial blockchain. Vitalik Buterin, founder of Ethereum, and subsequently the development team opted to go with the hard fork and operate on what’s now “Ethereum” today.
Read more about What is Ethereum Classic?
15. NEO (NEO)
A top platform for smart contracts and occasionally referred to as “China’s Ethereum.” NEO (officially Antshares) expects to digitize various forms of resources that were formerly kept in more conventional means, and so make it feasible to utilize them in smart contracts.
To envision a potential use case of NEO, consider digitizing the name to a house to a wise advantage, then setting up that asset to automatically transfer to a different person after payment for the home was received. This would be, in effect, a simple smart contract.
NEO founder Da Hongfei is a leading body in the cryptocurrency world, and it has worked on several blockchain jobs previously. The development team is made up of 6 in-house investors and a large community of third-party programmers.
Read more about What is NEO?
16. Binance Coin (BNB)
Binance Coin is the coin used to facilitate operations around the Binance system, a cryptocurrency market that’s capable of processing 1.4 million orders per second. The name “Binance” is derived from the combination of the terms “binary” and “finance,” referring to the integration of digital technology and fund.
The BNB coin is used to cover exchange fees, withdrawal fees, listing fees, and the rest of the possible trade expenses on the Binance platform. To be able to incentivize new customers to perform their cryptocurrency trading on Binance, the group is offering discounts when BNB is used to cover fees. The reduction will be 50% in the first year, 25% in the second, 12.5% at the third, and 6.25% in the fourth year prior to the discount ends.
Binance was mostly marketed to Chinese cryptocurrency investors initially, but they also have English, Korean, Japanese, French, Spanish, and Russian versions of this platform.
Read more on What is Binance Coin?
17. NEM (XEM)
NEM (New Economy Movement) is the world’s first Proof-of-Importance (PoI) enterprise built on the blockchain technology. With a concentration on business use cases, the program was built from the ground up with adaptability in mind. NEM’s aim is for companies to utilize their “smart asset system” to execute customizable blockchains. A wise asset could be almost anything: a cryptocurrency token, a company’s stock or a business’s invoicing and documents.
Some possible use cases for NEM’s technology include voting, crowdfunding, inventory ownership, keeping protected records, loyalty rewards point applications, mobile payments and escrow services.
The Growth of NEM is monitored by the Singapore-based NEM Foundation.
Read more on What is NEM?
18. VeChain (VET)
As described in VeChain’s growth plan, the organization’s purpose is to construct “a trust-free and distributed business ecosystem based on the Blockchain technology self-circulated and expanding.”
They plan to do that by producing an efficient trustless small business ecosystem to greatly reduce the ineffective information transport systems of now.
Some of the places and industries the VeChain platform is focusing on include eliminating counterfeiting in the fashion and luxury industry, food safety tracking systems, digitizing maintenance in the vehicle industry and several other worldwide supply chain processes.
Read more on What is VeChain?
19. Tezos (XTZ)
Tezos is a smart contracts platform hot off their exceptionally successful and contentious ICO. Tezos is currently working to create a cryptocurrency “commonwealth” in which the holders of XTZ tokens have the ability to vote in new protocols, which will effectively give users complete control over the future of the blockchain.
In addition, this permits for Tezos methods to change and improve overtime, instead of requiring the radical changes every now and then that tend to lead to challenging forks.
With Tezos, users can vote for rewards to be allocated to programmers who are making excellent contributions to jobs, and therefore incentivizing the growth of the platform.
Tezos has a few technological differences compared to Ethereum like using dPoS, the exceptional ability to upgrade without needing a fork, and proper confirmation which allows for code to be mathematically proven to be correct. This is very beneficial in the case of sensitive calculations needed in fields like aircraft design and atomic development.
Read more on What is Tezos?
20. Zcash (ZEC)
Zcash is a worth transfer protocol forked off the Bitcoin blockchain. Zcash can be utilized like Bitcoin, with a few additional improvements. With “zero cash technologies,” Zcash protects the amount transferred and the senders, making trades truly anonymous.
Zcash is one of those newest kids on the block from the world of “private trades”
An interesting note is that Ethereum is in the process of implementing some of Zcash’s technologies to allow trades on the Ethereum network to be anonymous too.
Zcash has been developed by the Zerocoin Electric Coin Company. They have had some fantastic successes, most notably JP Morgan’s announcement that they’d apply Zcash’s privacy technology to Quarum, a tech JP constructed on Ethereum.
Read more about What is Zcash?
Bonus coin: DOGECOIN (DOGE)
Dogecoin is a peer-to-peer digital payment system based on the popular 2013 meme of the Shiba Inu dog. It was a branch of Luckycoin, which was a fork of Litecoin. The coin uses a PoW script mining algorithm very similar to Bitcoin; nonetheless, while Bitcoin includes a restricted number of coins, there’s absolutely no limit to the amount of Dogecoins which can be created. The current rate of Dogecoin creation is over 5,000,000,000 coins per year.
Dogecoin is among the oldest altcoins in life, and for that reason, they possess a relatively large community. The Reddit webpage has about 90,000 shibes (the group name to get their community members).
Dogecoin is a great coin to utilize for microtransactions and is commonly used for tipping on articles. The coin is a kind of self-proclaimed “joke coin” that has gained a lot of popularity.

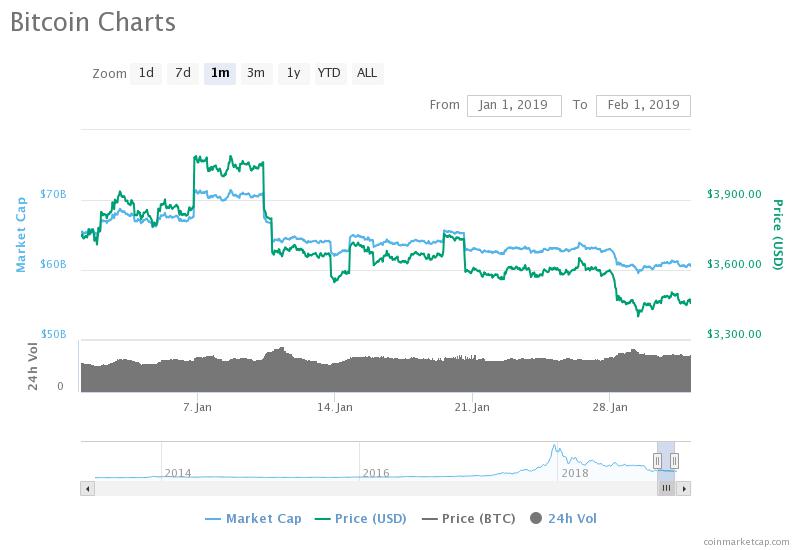
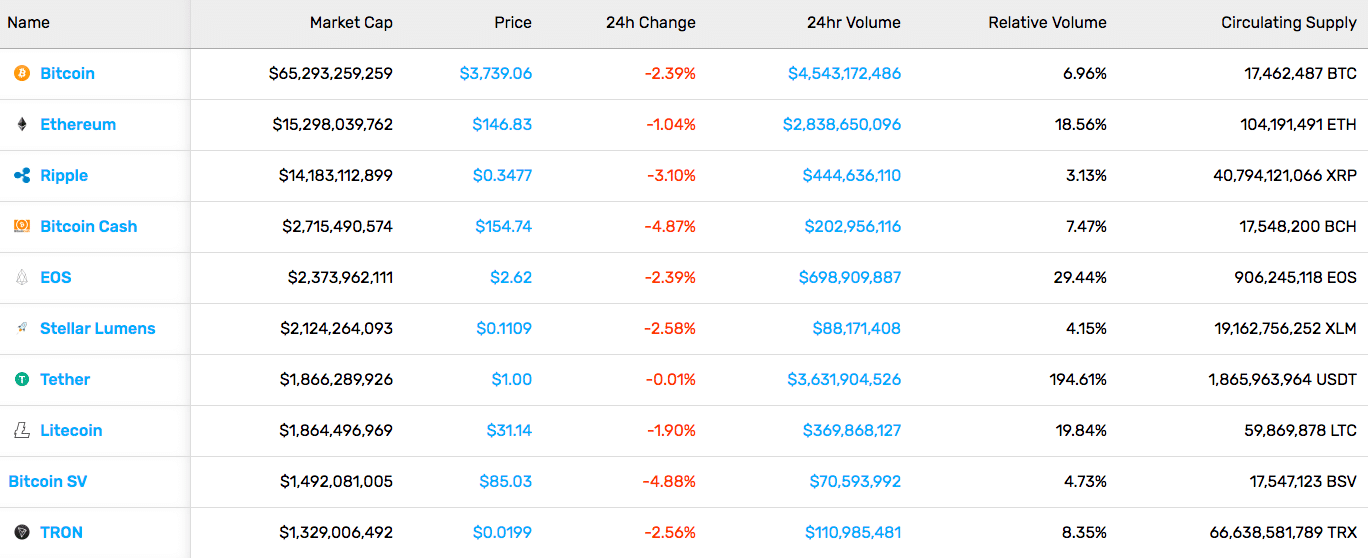 The second week of January left us with a drop in the crypto market, with a $123.2B market cap, a 4.5% drop on the week. Most of the top cryptocurrencies saw red during this week as well, with the exception of Tron (TRX) which actually grew 23.71%.
The second week of January left us with a drop in the crypto market, with a $123.2B market cap, a 4.5% drop on the week. Most of the top cryptocurrencies saw red during this week as well, with the exception of Tron (TRX) which actually grew 23.71%.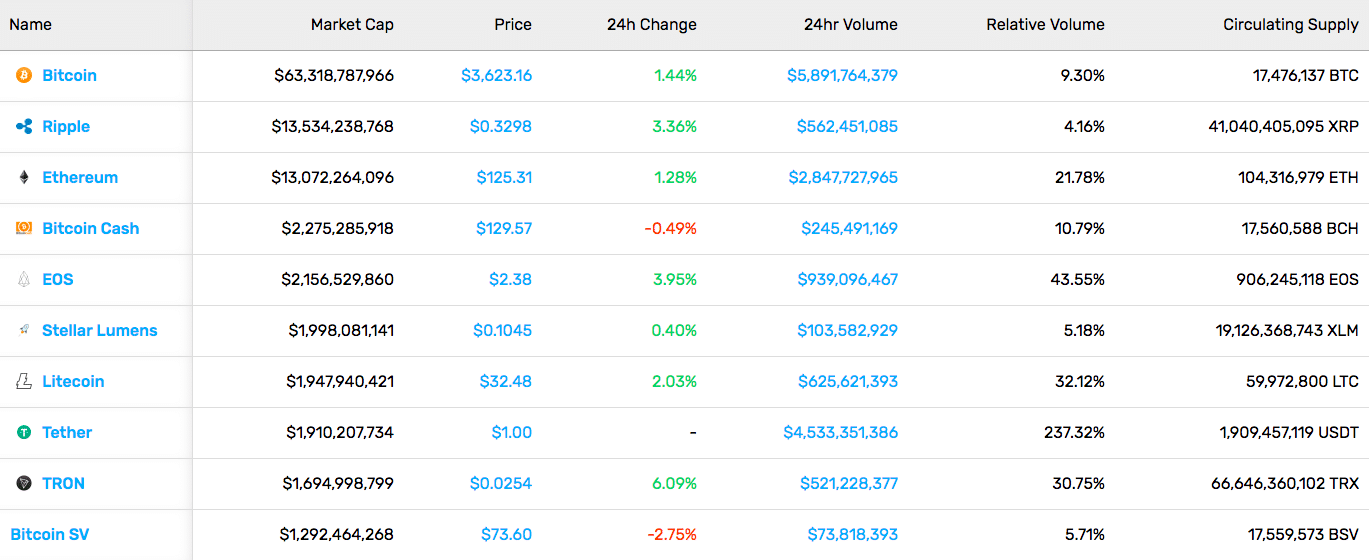 A rather uneventful week was the third week of the year. The total market cap was at around $122B. Most individual cryptocurrencies stayed within single-digit gains and losses. A few exceptions were Augur (56.85%), Chainlink (20.45%), and TenX (78.94%).
A rather uneventful week was the third week of the year. The total market cap was at around $122B. Most individual cryptocurrencies stayed within single-digit gains and losses. A few exceptions were Augur (56.85%), Chainlink (20.45%), and TenX (78.94%).