What is NEM?
According to the NEM website:
Blockchain technology offers a fundamentally streamlined method of maintaining a secure ledger of transactions compared to a traditional database.
The NEM vision is stated from the beginning of their whitepaper, which is referred to as a Technical reference.
NEM is a movement that aims to empower individuals by creating a new economy based on the principles of decentralization, financial freedom, and equality of opportunity.
We would like to thank the contributors and the many people who have inspired us. . .
BloodyRookie gimre Jaguar0625 Makoto
| Denominations | |
|---|---|
| Subunit | |
| 0.000001 | µXEM (microXEM) – smallest unit |
| 0.001 | mXEM (milliXEM) – thousandth unit |
| Plural | XEM |
| Symbol | XEM |
| Demographics | |
| Date of introduction | 31 March 2015 |
| User(s) | Global |
| Issuance | |
| Issuer | Fixed Decentralized peer-to-peer consensus |
| Website | NEM |
| Valuation | |
| Genesis Block Production | Fixed 8,999,999,999 XEM total |
|
Block time 1 minute
Technology Blockchain |
|
New Economy Movement (NEM) is an enterprise-grade solution to power the impending blockchain market. Initially meant to be a branch of NXT, but the NEM community chose to go with an entirely new codebase with an alpha version published June 25, 2014, and also the initial stable release March 31, 2015.
Focus on constructing just what you require, whether that is a fintech system, monitoring logistics, an ICO, record notarization, decentralized authentication, or even a whole lot more.
The Smart Asset System
The NEM blockchain powers what they call the Smart Asset System.
This system is meant to become an open, customizable blockchain alternative for virtually any variety of use cases assembled in addition to easy, effective API calls. The blockchain is procured and trades are processed with a worldwide network of nodes operating the NEM core applications, and the system is employed as an API Gateway server.
This means developers seeking to build blockchain powered programs do not have to conduct any distinctive NEM applications as each the NEM performance can be found by obtaining API calls.
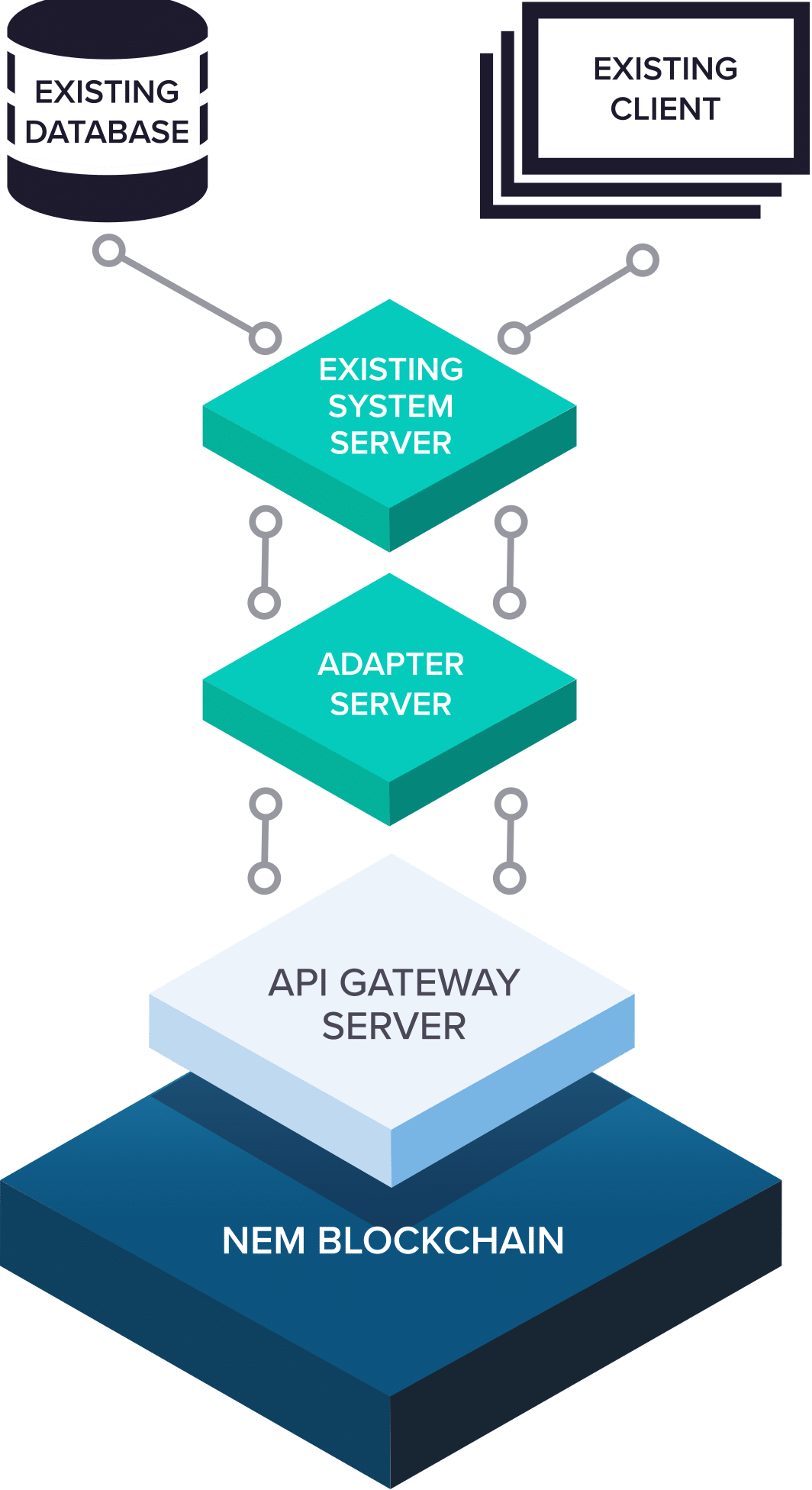
This allows for a great deal of flexibility in regards to system design and the way many apps are using this NEM network. Programs can get the NEM API directly, get into another server as well as creating NEM asks, or current servers may be adapted to use NEM in the backdrop.
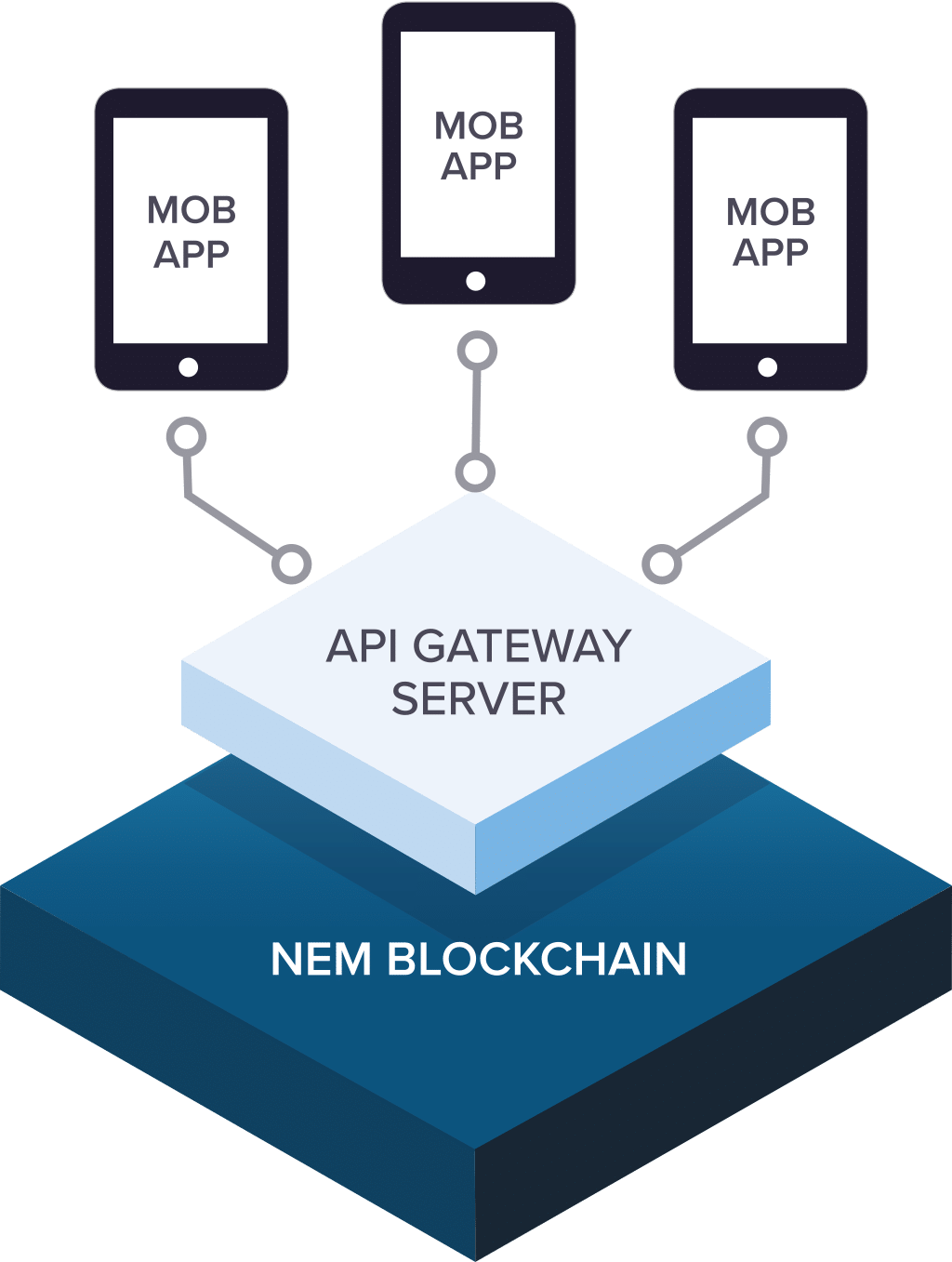

Programmers define NEM Addresses that act as containers for resources and could be upgraded and altered over time. An Address could signify simply a pocket holding coins or something more complex like a record which needs an election that’s collecting votes.
The programmer would then produce Mosaics: indistinguishable, transferable resources which represent the signatures, coins, or votes which will live in the Addresses. This system of adaptive addresses and configurable mosaics is feasible for countless use instances, and because each one the NEM performance is obtained via the NEM API, anyone can construct any type of system that they wind up and hook it in the NEM blockchain with relative ease.
Proof-of-Importance and Harvesting
The NEM Blockchain employs a Proof-of-Importance algorithm (as opposed to Bitcoin’s Proof-of-Work or PIVX’s Proof-of-Stake) to achieve consensus through a process that incentivizes active participation in the network.
This generates a decentralized, nimble community of well-behaved nodes.
Part of the system operates by vesting coins: whenever you put coins on your pocket, they begin as unvested coins.
As time passes, your coins will start to vest or rely on the significance of your accounts.
This region of the system functions like staking coins in PoS instalments but is just 1 part of calculating your own importance.
Along with monitoring vesting, the trade chart of the NEM system is continually analyzed to give information on which nodes are leading and which aren’t. This usually means that the more trades you send to other customers and the longer you use the system generally, the more important you become. The vesting procedure and transaction metrics lead to a significance score for every node, and these scores are utilized to scale the odds of your node harvesting XEM.
Since PoI isn’t hardware intensive, so it permits full nodes to be run on just about any machine irrespective of electricity, preventing centralization of harvesting to people with the largest machines.
As it takes a time commitment via the vesting procedure, it prevents the”rich get richer” effect of numerous staking systems wherein individuals with the most cash instantly turn into the largest earners and cannot be outpaced.
In certain systems such as Bitcoin, mining cubes and directing a community node are different. From the NEM system, running a node to guarantee the system and reaping coins is accomplished by precisely the exact same applications, incentivizing conducting a complete node and contributing to more decentralization over time since harvesting becomes more rewarding.
The PoI process is exceptional and can be an alternative to conventional consensus methods that come with their share of advantages and flaws.
NEM Blockchain Features
NEM employs a customized version of the Eigentrust++ algorithm which implements a”reputation system” for nodes on the community. Fundamentally, every node keeps track of the data that it receives from other nodes (fresh cubes, trades, etc.) and subsequently confirms this information.
If the information shows valid, the standing of the supplying node increases, and when it is bad information the standing will decrease. The reputations of nodes are passed across the community and updated inside each node. This allows for automatic load balancing and eliminating bad nodes in the community, keeping the system running as easily and fast as possible.
Additional Features:
- Constructed spam filters Which prevent Junk transactions from Flood the System and clogging up the Functions
- A P2P time synchronization system Which Allows the System to Keep accurate timestamps without relying upon any External servers for Assessing time
- Encrypted messaging onto the blockchain without Breaking Trade fields to Transmit Info like other coins
- Multisignature addresses Enable Programmers to Specify shared addresses and multiparty control over Resources and containers
Information on the technology described here and can be found on the NEM technology page and in more technical detail in their technical reference.
Public vs. Private
Everyone may use the people NEM blockchain by taking advantage of their API calls, but also for programs that need more privacy or want to store things in house, a personal version of the NEM blockchain may be provisioned to operate on servers that are internal and just take advantage of predefined nodes of their consumers’ choosing. On such trusted, personal node networks, a few characteristics of this public network which are in place to stop bad nodes from inducing difficulties can be eliminated or reused in extent, allowing for much quicker transactions (to the thousands/second) at a closed box installation.
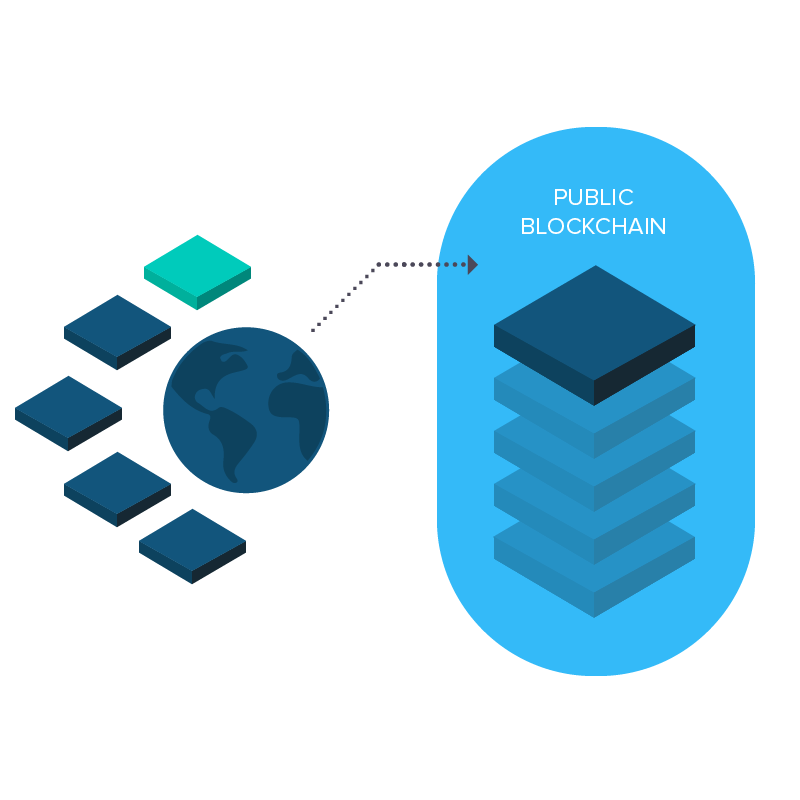
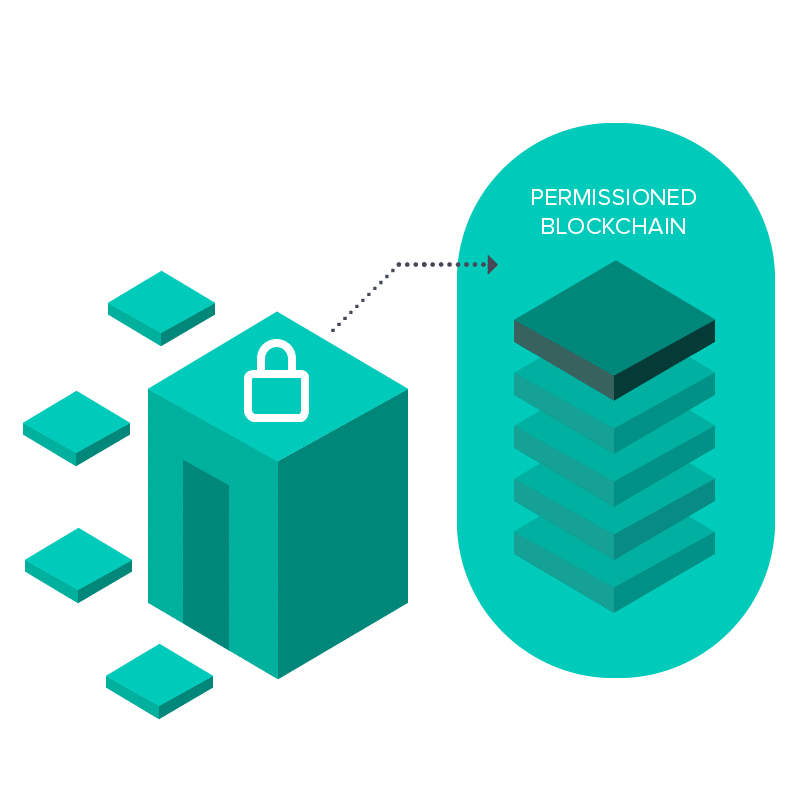
These personal blockchain deployments may be used to power anything from loyalty points plans to transport fleet logistics, without exposing the trade information and supplying unparalleled speed and safety. This creates a good deal of sense for businesses which are looking to utilize the blockchain to power their present internal tools and also do not require the additional performance of their general public series. Use cases for the NEM system private and public are researched on their site at http://nem.io/enterprise/.

