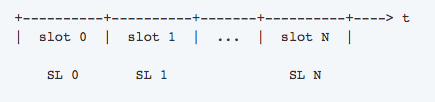What is Cardano?
Very similar to Ethereum, Cardano is a wise contract platform nonetheless, Cardano provides scalability and safety through a layered structure.
The official Cardano.org website states:
Cardano is more than just a cryptocurrency, however, it is a technological platform that will be capable of running financial applications currently used every day by individuals, organisations and governments all around the world. The platform is being constructed in layers, which gives the system the flexibility to be more easily maintained and allow for upgrades by way of soft forks. After the settlement layer that will run Ada is complete, a separate computing layer will be built to handle smart contracts, the digital legal agreements that will underpin future commerce and business. Cardano will also run decentralised applications, or dapps, services not controlled by any single party but instead operate on a blockchain.
Why is Cardano special? Cardano is exceptional as it’s constructed on scientific doctrine and peer-to-peer academic study.
The Origins of Cardano
Cardano was conceptualized by Charles Hoskinson who appears to be among those co-founders of all Ethereum.
Ethereum remains praised for its clever contract stage. However, Hoskinson states it’s a second creation blockchain (more about this later) and desired development. Why is Cardano remarkable is that the sheer quantity of maintenance that goes to its own upkeep. There are 3 associations that work full time to develop and treat Cardano: The Cardano Foundation, IOHK, Emurgo.
The Cardano Foundation is a non-profit regulated entity that’s the custodial business of Cardano. Their principal purpose is to “standardize, protect, and promote the Cardano Protocol technology”.
In 2015, combined with Jeremy Wood, Hoskinson discovered IOHK (Input Signal Hong Kong). IOHK is a”research and development firm committed to utilizing the peer-to-peer creations of blockchain to construct accessible financial services for everybody.” They’ve been contracted to construct, design, and preserve Cardano till 2020.
Emurgo is a Japanese firm that “develops, supports, and incubates commercial ventures who want to revolutionize their industries using the blockchain technology.” A lot of IOHK’s financing comes from a 5-year contract with Emurgo.
These three organizations work in synergy to be certain that Cardano growth is happening at a fantastic pace. Cardano explains itself as a 3rd generation blockchain.
The Three Generations of Blockchain
According to Charles Hoskinson, we’ve gone through three generations of blockchains.
Generation 1: Bitcoin and Money Transfer
Bitcoin was made because everybody was asking exactly the very same questions.
Can it be possible to make a type of cash that could be moved between two individuals with no middleman?
Can it be possible to make decentralized money that may function on something such as the blockchain?
Satoshi Nakamoto answered these concerns when he generated bitcoin. We had a decentralized financial system that could transfer cash from 1 individual to another.
But, there was an issue with bitcoin that is a problem with first production blockchains. They just permitted for financial transactions, there wasn’t any method to include terms to these trades.
Alice can send Bob 5 BTC, but she could not impose terms to these trades. Eg. She could not tell Bob that he’ll find the money only if he played specific jobs.
These conditions could require extremely complicated scripting. Something was required to make the process simpler.
Generation 2: Ethereum and Smart Contracts
What is a smart contract?
Smart contracts enable you to trade cash, land, stocks, or anything of worth in a transparent, conflict-free manner whilst preventing the assistance of a middleman.
Vitalik Buterin’s Ethereum can be readily the stalwart of the creation. They showed the world the way the blockchain could evolve from an easy payment mechanism to something a lot more meaningful and strong.
This creation had some issues also.
As more and more interesting use instances of these blockchain were coming out, they had been becoming an increasing number of acceptance.
The problem was these generations of blockchain did not have great consequences for scalability. Together with that, the government system of those blockchains weren’t actually that well thought out. Case in point, the Ethereum and Ethereum Vintage divide, based on Hoskinson, is a classic case of terrible governance.
Generation 3: Cardano
Hoskinson understood the blockchain required to evolve more. He took the favourable elements in the first two centuries of blockchain and included several parts of his own.
The 3 components that Cardano desired to resolve were:
- Scalability.
- Interoperability.
- Sustainability.
Cardano is exceptional in the sense it is developed on scientific doctrine and peer-reviewed academic study. Each of the technology that goes to it gets the ultimate aim of becoming”High Assurance Code”. This is done in order to be certain there is far higher belief in the character of the code used (more about this later when from the”Haskell and Plutus” segment ). This, based on Hoskinson, will stop future cases such as the ETH-ETC divide from occurring.
The Philosophy of Cardano
The Cardano team would like to stick to some principles and principles. They didn’t put out with a suitable roadmap or even a white paper. Rather, they concentrated on adopting a”set of layout principles, engineering best practices, and paths for exploration.”
These are the following principles and they’re taken straight from the Cardano site.
- Separation of bookkeeping and computation into various layers.
- Implementation of core elements in a highly modular operational code
- Small groups of professors and programmers competing with peer study research
- Substantial utilization of interdisciplinary teams such as ancient usage of InfoSec specialists
- Quick iteration involving white papers, execution and fresh study necessary to fix issues found during an inspection
- Construction from the capability to update post-deployed systems without ruining the system
- Development of a decentralized financing mechanism for future job
- A long-term perspective on enhancing the plan of cryptocurrencies in order that they could work on cellular devices using a secure and reasonable user experience
- Bringing stakeholders nearer into the operations and upkeep of the cryptocurrency
- Acknowledging the necessity to account for numerous resources at precisely the exact same ledger
- Abstracting trades to add discretionary metadata in order to better conform to the demands of heritage methods
- Learning in the almost 1,000 altcoins by adopting characteristics which make feel create a standards-driven procedure inspired by the Internet Engineering Task Force with a committed base to lock the last protocol layout
- Research the societal elements of trade locate a wholesome middle ground for labs to socialize with trade without undermining some core principles inherited from Bitcoin.
Element #1: Scalability
“Scalability” allows you to think of transactions processed each minute or throughput. In accordance with Hoskinson, that is only 1 part of the issue. Overall scalability is a three-headed issue. You Need to take good care of three different components:
- Transactions a minute / Throughput
- Network.
- Data Scaling.
#1 Throughput
Many articles are written about the dearth of throughput in Bitcoin and Ethereum. Bitcoin oversees 7 trades per minute and Ethereum oversees 15-20. This isn’t suitable for a monetary system.
Cardano expects to fix this issue by using their consensus mechanics, Ouroboros. It’s a provably secure proof-of-stake algorithm. Ouroboros was really peer-reviewed and accepted throughout Crypto 2017.
Ouroboros, as mentioned previously is a proof-of-stake algorithm.
Bitcoin and Ethereum follow the proof-of-work protocol.
Proof-of-work for a procedure has the following steps for this:
- The miners fix cryptographic puzzles to”mine” a block so as to increase the blockchain.
- This procedure requires a massive quantity of power and computational use. The puzzles are made in a way that makes it difficult and taxing on the system.
- When a miner simplifies the mystery, they pose their block into the community for affirmation.
- Verifying if the block is owned by the series or not is a very simple procedure.
That, basically, is exactly what the proof-of-work program is. Solving the mystery is tough but assessing whether the remedy is really right or not is simple. This is actually the system that Bitcoin and Ethereum (till today ) have already been using. But, there are a number of basic flaws in the system.
The problem with proof of work.
As it happens, there are a number of issues with proof-of-work.
- First and foremost, evidence of work is a very inefficient process due to the sheer quantity of energy and power that it occupies.
- Individuals and organizations who may afford quicker and stronger ASICs normally have a higher prospect of mining compared to others.
- As a consequence of this, bitcoin is not as decentralized as it needs to be. Let us assess the hashrate distribution chart:
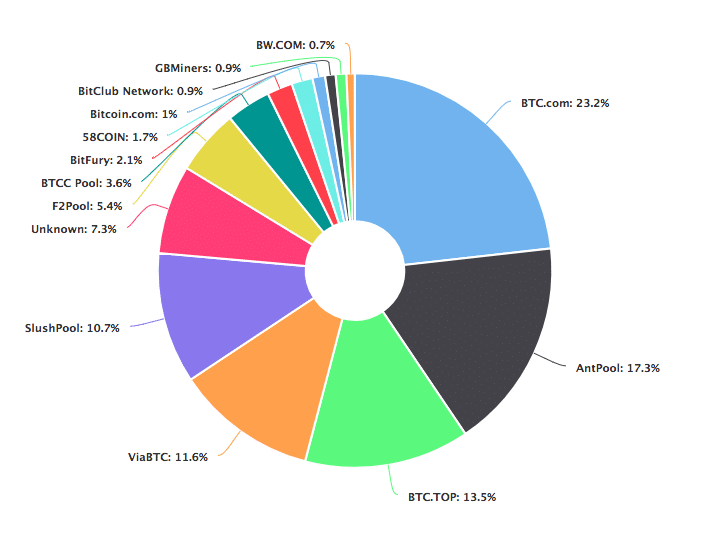 Image Credit: Blockchain.info
Image Credit: Blockchain.info
Approx 75 percent of this hashrate is split among 5 mining pools independently.
- Theoretically speaking, these significant mining pools can merely team up with one another and establish a 51% over the bitcoin network.
To fix these issues, Ethereum appeared to Proof of Stake as a remedy.
What is proof of stake?
Proof of bet is likely to make the whole mining process virtual and substitute miners with validators.
Here is how the procedure works:
- The validators might need to lock up a number of their coins as bet.
- Then, they will begin validating the cubes. Meaning, when they find a cube that they think could be added to the series, they will affirm it by putting a wager on it.
- When the block becomes appended, then the validators will find a reward proportionate to his or her bets.
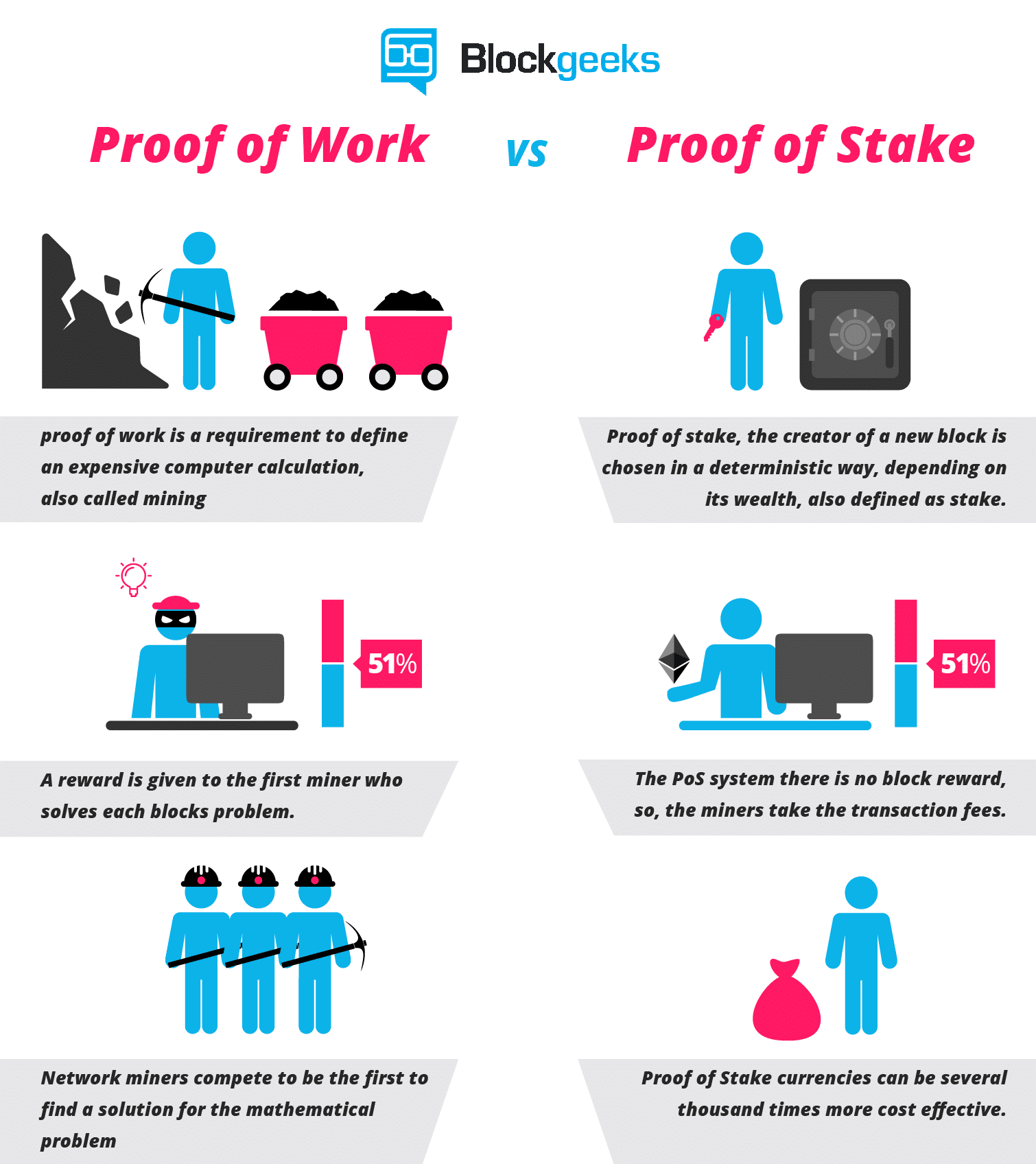
Image blockgeeks.com
Cardano: Ouroboros Underneath the Hood
Ouroboros appears at the origin of these tokens in the ecosystem and by a supply of random numbers, it divides the planet into epochs. Each epoch is subsequently broken up into slots. Every epoch lasts for an extremely short time ~20 minutes.
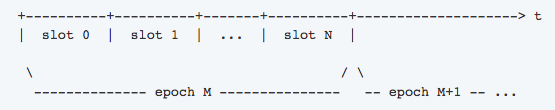
Image credit: Cardano Docs
Each slot subsequently gets its own slot boss, who’s randomly selected.
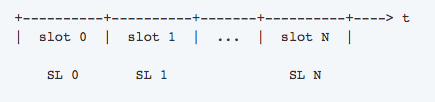
The Slot leader behave like miners does at a POW protocol in the sense they are the people who opt for the blocks which get added into the blockchain. They can, however, add just 1 block.

If a slot boss misses their luck and does not opt for the cube, they miss their chance and might need to wait until they become winners . It’s okay for one or more slots to stay vacant (without created cubes ), but the vast majority of the cubes (at least 50 percent + 1) have to be generated through an epoch.
As you can see, the slot pioneers have an essential function to play in the ecosystem. To be considered for eligibility, an individual has to have 2 percent stake in Cardano. These stakeholders are known as electors and they’re those who select the slot leaders to another epoch through the present epoch. The more wager that the stakeholder has from the machine, the greater chance they have to get chosen as slot leaders.
Now, because the slot leaders have a great deal of power, particular care has to be taken to make the election as impartial as you can. There have to be a certain quantity of randomness involved. That is the reason a multiparty computation (MPC) is performed to attain some kind of randomness.
Inside this MPC strategy, each elector plays a random action referred to as”coin tossing” and then stocks their outcomes together with other electors. Although the outcomes are randomly created by every elector, they agree on the exact same closing price.
The election is divided into three phases:
- Commitment Phase.
- Reveal Phase
- Recovery Phase.
Commitment Phase
Primarily, an elector creates a secret random value and forms a”devotion”. The devotion is a message which has encrypted stocks (keep this in mind for your own retrieval period ) along with a proof of key.
Following that, an elector signals the devotion with their private key and defines the epoch number and attaches their public key. Doing so solves two functions:
- Everyone can assess who generated this devotion (because it’s the public key attached to it).
- They could assess which epoch it belongs to.
Following this is completed, the elector sends their responsibilities to additional electors. Finally, each elector hastens another elector’s responsibilities (The responsibilities become placed to the cube and eventually become part of their blockchain).
Reveal Phase
Think of obligations such as a locked box which has a secret inside and there’s a particular significance that unlocks the box. This particular value is known as an”opening”. That is exactly what this stage is about, the more electors ship their”opening”. These openings can also be placed to the block and becomes a part of this blockchain.
Recovery Phase
By this time, an elector has both openings and obligations. But some electors may behave maliciously and release their own devotion with no opening. Fundamentally, give the locked box with no passphrase.
To be able to circumnavigate this, the frank electors can post each of the encoded stocks (as mentioned at the dedication phase) and just rebuild the keys. In this manner, even if specific electors behave in a malicious way, the machine will still operate. This is the way Ouroboros has its Byzantine Fault Tolerance.
Finally, an elector confirms the responsibilities and openings fit and when that occurs, the keys from the responsibilities are extracted which creates a seed. The seed is a randomly generated byte chain.
Each of the electors now have this particular seed.
We’re picking slot leaders to another epoch. To be able to be certain the election is as impartial as possible we had some kind of randomness. The”seed” supplies us with this randomness. Now it’s time to pick the Slot Leaders.
To do that we’ll utilize the Follow the Satoshi (FTS) algorithm.
Cardano: The FTS Algorithm
The title of this algorithm stems in Satoshi Nakamoto, the unknown founder of Bitcoin.

Image credit: Cardano Docs
The FTS basically chooses a random coin in the bet. Whoever owns that coin becomes the slot pioneer. It’s that straightforward!
That is the reason why, the more bet one has from the machine, the more opportunities they have of winning this lottery.
The slot leaders may have the ability to not just select the cubes in the most important blockchain except to select blocks in different blockchains within the Cardano ecosystem too.
#2 Network
Just just how can Network variable into scalability?
Straightforward… bandwidth.
The trades carry info. Whilst the amount of trades increases so will the demand for community resources.
The idea is really simple: When a system is to climb to millions of consumers, the system will require 100s of terabytes or even exabytes of tools to sustain itself.
As such, it is impossible to maintain a homogenous network topology. What does that mean?
At a homogenous network topology, each node in the system relays every single message. Skype is a good instance of such a system where the majority of the value is obtained from one category of consumers that are interested in placing a telephone call.
In a decentralized community, that could become impractical for scaling up. Each of the nodes might not have the tools needed to relay the info in an effective way.
To fix this matter, Cardano is considering a new kind of technology named RINA, Recursive Inter-Network Architecture made by John Day. It’s a new sort of structuring networks with policies and innovative engineering fundamentals.
RINA’s goal is to create a heterogeneous network which promises to give:
- Privacy.
- Transparency.
- Scalability.
It does so in a sense where you are able to guess the way the system will arrange in an official capacity. It’s hoped it will easily interoperate using TCP/IP protocols. Cardano expects to execute this in part by 2018 and by 2019.
According to Wikipedia:
RINA inherently supports mobility, multi-homing and Quality of Service without the need for extra mechanisms, provides a secure and programmable environment, motivates for a more competitive marketplace, and allows for a seamless adoption.
#3 Data Scaling
Blockchains store items for eternity. Every tiny bit of information, applicable or not becoming saved in the blockchain for eternity. Since the system scales up and an increasing number of folks come in, using the absolute influx of information that the blockchain gets increasingly more bulkier.
Now, keep in mind a blockchain runs since it includes of Nodes. Every node is an individual that stores a duplicate of the blockchain inside their machine.
Since the blockchain gets warmer, it is going to require additional space, and that’s unreasonable for a standard user using a regular computer.
The way Cardano Would like to solve This Issue is by implementing a straightforward philosophy, “Not everyone needs all the data.”
E.g. if Alice and Bob engage in a transaction, it may not be relevant to anyone else in the network. The only thing they need to know is that the transaction happened and that it was legitimate.
The techniques that Cardano is looking into are:
- Pruning.
- Subscriptions
- Compression.
If they’re applied properly, then it could actually substantially lessen the number of information a user wants to possess.
In addition to this, there’s also the idea of Partitioning. Rather than having an entire blockchain, an individual may easily have a chunk of their blockchain and significantly lessen the number of information they will need to save.
Cardano’s goal here would be to use this info to compress the information that the users will need to eat without compromising on safety or the assurances that their trades have gone through correctly.
Element #2: Interoperability
Today we’ve seen how the Scalability facet of Cardano functions, we now arrive at the second pillar: Interoperability. The short and long of interoperability isalso, as Charles Hoskinson puts it, there will not be a single token to rule them all.
Let us look at the present ecosystem. From the cryptosphere, we’ve got distinct crypto coins like Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin etc.. In the same way, from the heritage financial world, we’ve got systems such as the conventional Banks that use SWIFT, ACH etc..
The issue is in the fact it is very hard for all these individual entities to communicate together. It’s hard for bitcoin to understand what’s happening in Ethereum and vice-versa. This becomes difficult when banks attempt to communicate with all the cryptos.
That is the reason why, the crypto markets, that provide a gateway involving cryptos and banks get so effective and important. But there in itself is still a problem. Exchanges aren’t a decentralized thing and are really vulnerable.
- They could get hacked.
- They could blackout for extended intervals for method upgradation. That is essentially what happened to Binance recently.
Additionally, there’s another place in which this miscommunication between the legacy world and the crypto world may result in a devastating effect: ICOs.
In ICOs, a thing has tens of thousands of dollars in exchange for their tokens, nevertheless, saving that money in their bank account may get difficult. The banks would clearly wish to understand where all of that cash came out and who had been the individuals who provided that cash that’s something which is not as likely to supply.
A more tasteful and secure solution to interoperability has been required.
A third-generation crypto coin has to offer an ecosystem where every person blockchain can communicate with a different blockchain and with outside legacy financial systems.
The Crypto World: Inter-Chain Communication and SideChains
Cardano’s vision is to create an “internet of blockchains”. Envision an ecosystem in which Bitcoin can stream into Ethereum and Ripple can easily stream into Litecoin with no need to undergo centralized exchanges. That is the reason why cross-chain transfers are something that Cardano would like to execute with no middlemen.
1 way that Cardano would like to do this is by applying sidechains.
Sidechain as a theory was at the crypto circles for quite a while now. The notion is quite simple; you get a parallel series which runs together with the principal string. The side chain is going to be attached to the main chain using a two-way recoil.
Cardano will encourage sidechains dependent on the study by Kiayias, Miller, and Zindros (KMZ) between “non-interactive proofs of proofs of work”.
According to Hoskinson, the idea of sidechains comes from two things:
- Getting a compressed version of a blockchain.
- Creating interoperability between chains.
The Legacy World: Bridging the Gap
When it comes to increasing the interoperability with the legacy world, Cardano wants to focus on the three obstacles that make the crypto world incompatible with the legacy world:
- Metadata.
- Attribution.
- Compliance.
Obstacle #1: Metadata
Metadata means the story behind the transaction.
If Alice were to spend 50 USD, the metadata of that could be as follows:
- What did Alice spend the money on?
- Who did Alice give that money to?
- Where did she spend the money?
While that is not that well planned out in the cryptocurrency space, it is extremely essential in the legacy banking world. In fact, this is one of the main reasons why most entities struggle post ICOs. They simply don’t have the metadata required to provide the banks.
In the legacy world, the metadata is extremely important. Here are the purposes that it serves:
- Resource discovery and identification.
- Effective electronic data organization.
- Tells us how data is exchanged among various systems and hence improves interoperability.
- Very useful in resource protection. Helps identify the data’s characteristics and behaviour for it to be replicated if needed.
The problem with metadata is that it is extremely personal and since the data is stored in the blockchain on a permanent and transparent basis, we have a situation where extremely private information can be permanently affixed to the blockchain.
One of the main things that Cardano is researching on is how to selectively attach metadata to the chain.
Obstacle #2: Attribution
Similar to metadata, via attribution the names of the people involved in the transactions gets known. Basically, who all are a particular transaction attributed to?
If the blockchain permanently fixes attribution to itself, it will greatly compromise on the privacy of the individuals involved.
Hence, Cardano plans to empower their users to hand out attribution as and when it is required.
Obstacle #3: Compliance
The next barrier is”Compliance”.
Compliance includes factors such as KYC (Know Your Customer), AML (Anti Money Laundering), ATF (Anti Terrorist Financing) etc.. )
Compliance is utilized to examine the validity of a trade. Fundamentally, if Alice pays Bob $50, compliance is utilized to be certain the trade isn’t completed for any nefarious purposes.
Though the crypto world has not actually done much on the front, it’s very crucial in the banking world in which the history and validity of every trade has to be understood.
What Cardano is exploring on is the way to utilize Metadata and Attribution in combination with Compliance to assist their customers any time they should socialize with all the banks.
Element #3: Sustainability
In accordance with Hoskinson, this is hands down the toughest you to address. It essentially means, how is Cardano intending to cover future development and expansion?
When some advancement Has to Be performed from the machine and grants are needed, you will find a couple of things which can occur:
But the two of these have a problem.
With patronage, you’ve got the issue of a potential centralization. If a major company gives a large amount of grant into some blockchain business, they can direct the means by which the improvements turn out from the computer system.
With ICOs, it is just like a surprising jolt of cash with no sustainable version and it provides a whole unnecessary token into the ecosystem.
Something different and more sustainable has to be carried out.
In this way, Cardano will take inspiration from Dash and generate a treasury.
How will the treasury work?
Each time a block is inserted into the series, part of the block reward will be added into the treasury.
Consequently, if a person would like to grow and deliver some changes to the ecosystem, then they publish a ballot into the Treasury to request grants.
The stakeholders of this Cardano ecosystem afterwards vote and determine whether the ballot ought to be allowed or not.
If they do, the ballot submitter receives the grant for growth.
This program has a few important benefits:
- The treasury keeps on filling up because an increasing number of blocks are found.
- It’s directly proportional to the magnitude of this community. Larger the system, more the sources offered and also the voting system becomes much more decentralized.
But, there are a few barriers:
- An unbiased voting system has to be established.
- Voters should have an incentive to vote and take part in the system.
- Everybody’s vote must have some value to ensure a”Tragedy of Commons” type situation does not occur.
- The practice of submitting ballots ought to be simple and straightforward.
- The full procedure should be as straightforward as possible.
As of now, Cardano has recognized a system they can possibly use, which combines liquid democracy using an incentivized treasury model.
Cardano: how does liquid democracy work?
It is a system that fluidly transitions between direct democracy and representative democracy.
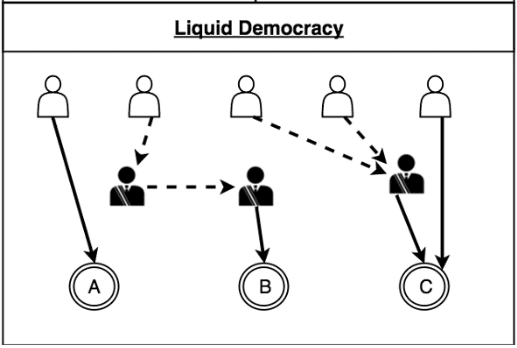
The Procedure has the following Attributes:
- People are able to vote their policies straight.
- People are able to assign their voting obligations to a delegate that can vote their policies to get them.
- The delegates themselves may assign their voting duties to another delegate who will vote in their behalf. This house wherein a delegate can decorate their very own delegate is known as transitivity.
- In case a individual, that has assigned their voting does not enjoy the vote which their delegates have picked, then they could take their vote back and vote on the coverage themselves.
Thus, what would be the benefits of liquid democracy?
- The view of every individual person counts and plays a role in the last policy creation.
- So as to be a delegate, all that one wants to do would be to acquire an individual’s trust. They do not have to spend countless dollars on costly election campaigns. As a result of this, the barrier to entry is comparatively low.
- Due to the choice to oscillate between assigned and direct democracy, minority groups could be fairly represented.
- Ultimately, it’s a scalable design. Anyone who does not have enough opportunity to vote their coverages can simply assign their voting obligations.
The Cardano ICO
The Cardano ICO raised about $62 million.
Cardano’s token is called Ada following Ada Lovelace, a 19th-century mathematician called the first computer programmer and daughter of the poet Lord Byron.
Cardano’s first significant release, called Byron, went live on September 29, 2017, which saw the initiation of the Cardano main-net.
Cardano fees
The fees to move ADA change is determined by the following formula:
Transfer fee = a + b * size.
Where:
a = A continuous which now equals 0.155381 ADA
b = Yet another continuous that now equals 0.000043946 ADA/byte
size = The size of the trade (in bytes0.
This effect means the minimal trade you will be paying is 0.155381 ADA and it’ll rise by 0.000043946 ADA for every byte growth of your trade size.
In every epoch, the trade fees are accumulated at a pool and contributed to the proper slot leaders.
Roadmap of Cardano
According to the roadmap, Cardano Will Probably be released in 5 Phases:
- Byron: Lets users to exchange and move Ada. The Cardano mainnet was launched.
- Shelley: Ensures that the technician is in place in order for it to turn into a totally decentralized and autonomous method
- Goguen: Can observe the integration of smart contracts.
- Basho: Determined around performance enhancements.
- Voltaire: IOHK will include a treasury system and governance.
Cardano: Conclusion
Cardano isn’t just built on solid doctrine, but also on hardcore science. In itself gives it a substantial advantage over its rivals.
The simple fact that somebody such as Charles Hoskinson is leading the way just adds more credibility. We’ll need to wait and watch until 2019 if they really can deliver all their lofty promises.

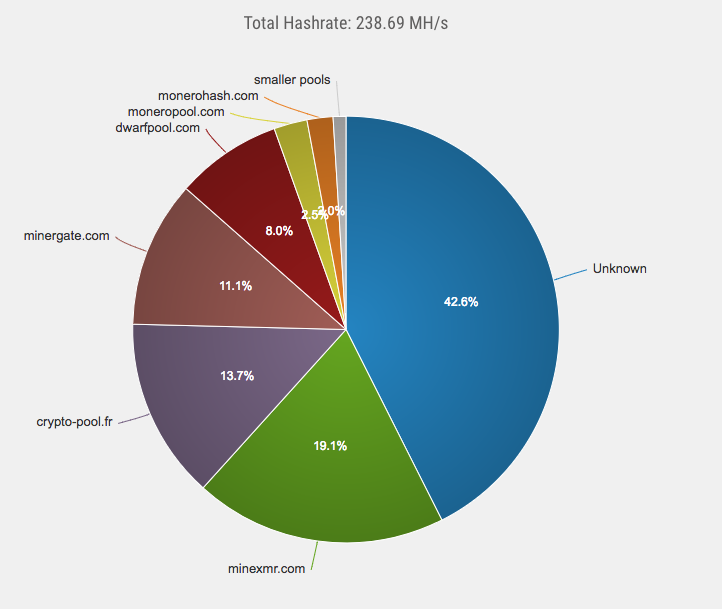


 Image Credit: Blockchain.info
Image Credit: Blockchain.info