The Ethereum Merge was completed one month ago. Since then, Ethereum centralization has been on the rise. More and more Ethereum nodes have been censoring the network. As of October 2022, 51% of Ethereum blocks were compliant with OFAC standards, which are meant to censor Ethereum’s blockchain.
What is OFAC?
OFAC, or Office of Foreign Assets Control, is a U.S. Treasury Department financial intelligence and enforcement agency. It enforces trade and economic sanctions to support U.S. foreign policy and national security objectives.
In August 2022, the crypto community was first acquainted with this agency when they issued a statement to sanction blockchain activities. It effectively sanctioned Tornado Cash as well as several Ethereum addresses that were associated with it.
Today, the number of nodes that are validating OFAC-compliant blocks is on the rise, and this represents a significant step towards censorship as more blocks are being monitored.
We reached another sad milestone in censorship: 51%
— Martin Köppelmann 🇺🇦 (@koeppelmann) October 14, 2022
This means if the censoring validators would now stop attesting to non-censoring blocks they would eventually form the canonical, 100% censoring chain. pic.twitter.com/JrYUjowLpt
The current state of compliant MEV-boost relays can be verified on mevwatch.info, a free tool built by Labrys.
MEV-Boost relays are centralized entities that act as trusted mediators between block builders and block producers. This allows all Ethereum proof of stake (PoS) validators to outsource their block productions to other builders.
This metric shows how many blocks have been built since the Merge by OFAC-compliant MEVBoost relays. MEV-Boost was able to provide a more representative distribution for block proposers than a small number of miners who are proof-of-work (PoW) after Ethereum upgraded to a PoS consensus.
Ethereum blocks went from 9% OFAC compliant to 51% OFAC compliant in the past month, as mev boost (block outsourcing) takes market share. https://t.co/SYiVHPlTf4
— Lyn Alden (@LynAldenContact) October 14, 2022
How is the OFAC involved with the Ethereum blockchain?
After “The Merge” upgrade was completed, the Ethereum blockchain started using the proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. This made the blockchain more secure and energy efficient. Mining data shows that Ethereum heavily relies on Flashbots, a single server, to build blocks. This raises concerns about a single point of failure for the blockchain.
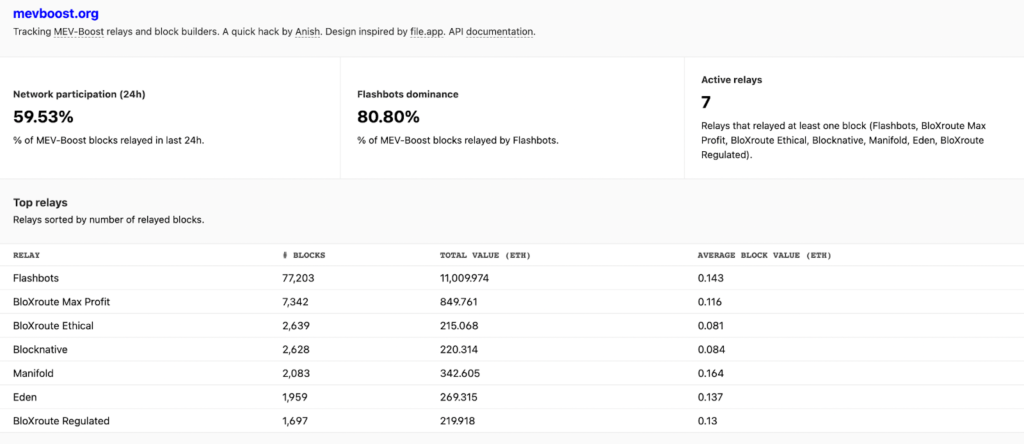
What is Flashbots? Flashbots is a network that connects mining pools and searchers. It’s not a closed system that uses private contracts or arrangements. Instead, anyone can join. Because it allows for competition, this open system is thought to be more beneficial than having a few dominant private entities. It acts as a relay to deliver Ethereum blocks. Data from mevboost.org indicates there are seven active relays currently delivering at most one block in Ethereum. These include Flashbots, BloXroute Max Profit, BloXroute Ethical, Blocknative, Manifold, Eden and BloXroute Regulated. 80% of MEV-Boost blocks are relayed by Flashbots.
What is Ethereum centralization? How can ETH transactions be censored?
Hard censorship would mean that no matter how long or how expensive you pay, sanctioned transactions will never be included in the blockchain. In a strict censorship scenario, compliant nodes would be required by regulation to discard all blocks with any of these transactions.
However, even with soft censorship, when approved transactions are eventually validated, it would likely lead to long waits, high-priority charges, and a substandard user experience.
Out of the seven major MEV-boost relays currently in operation (Flashbots, BloXroute Max Profit, BloXroute Ethical, Blocknative, Manifold, Eden, BloXroute Regulated), only three do not censor in accordance with OFAC compliance requirements. For instance, OFAC-compliant relays won’t include transactions that interacted with Tornado Cash smart contracts or other sanctioned wallet addresses, as defined by OFAC.
Validators that wish to include all network transactions can do so by not including any censoring relays in their MEV-boost configuration. Current major MEV-boost relays that don’t censor include – BloXroute Max Profit, BloxRoute Ethical, and Manifold.

