Did you know that you can claim Bitcoin hard forks coin if you owned Bitcoin at the moment of the fork?
Bitcoin, the first and most popular cryptocurrency ever created, has not been free from conflicts within the community. Over the years, many individuals and groups of developers have come up with ideas to make Bitcoin even better.
But most of these suggestions ended up dividing the community. That’s why over 100 Bitcoin hard forks have taken place since Bitcoin’s creation in 2009. Here’re the top BTC hard forks and how to claim them.
A Short History of Bitcoin
On October 31, 2008, a whitepaper was published that described the concept of Bitcoin ━ a trustless peer-to-peer system for digital currency to replace traditional money. The paper was published under the name of Satoshi Nakamoto, but the author’s identity remains a mystery to this day. Many believe that the name is a pseudonym of one or a team of developers.
On January 3, 2009, the genesis block (block 0) was mined on the Bitcoin network, and the miner, the unknown Satoshi, was rewarded with 50 bitcoins.
From that point on, Bitcoin (BTC) was mined by other early contributors up to 2010. Laszlo Hanyecz, a programmer, made the first commercial transaction using cryptocurrency by purchasing two Papa John’s Pizzas for 10,000 BTC.
Bitcoin has been traded many millions of times since then. The first major transactions were made in black markets. The largest was the Silk Road, an online black marketplace, which traded close to 10 million Bitcoin during its lifetime.
As Bitcoin grew more as a currency on different markets, regulations emerged from many countries. For instance, the People’s Bank of China (PBC) made the news headlines when they adopted these three separate actions and issued new regulations regarding cryptocurrencies.
- December 2013. The PBC banned financial institutions from using Bitcoin.
- September 2017. The PBC issued a total ban on Bitcoin use.
- June 2021. PBC implemented a crackdown against major cryptocurrency miners.
The price of Bitcoin fell by half after each of these events. However, it always found a way to rise again to new astonishing values. This is because many countries and institutions allow cryptocurrency use. Also, as of September 7, 2021, El Salvador became the first country in the world to adopt Bitcoin as legal tender.
Another aspect of what makes Bitcoin increase in price is the maximum supply. There can only be 21 million BTC. As more investors join the cryptocurrency market, the coin experiences scarcity and the Bitcoin (BTC) price surges as with any supply and demand market.
Additionally, Bitcoin is more transferable and divisible than gold or another material asset and can be stored more easily. It will cost you a lot to transport gold, as well as the cost of storage in secure facilities. However, investors can store Bitcoin on a USB stick, also known as a cold wallet or hardware wallet.
As Bitcoin gained more popularity, it inspired other developers to create other blockchain platforms, and subsequently, some created Bitcoin hard forks.
What is a Bitcoin fork?
Many of the cryptocurrencies that exist today use part of Satoshi’s technology. However, many others adapted the Bitcoin blockchain model or tried to improve it.
As more users joined the blockchain, it became increasingly difficult to update the network as no single person or group could decide on unanimous future development.
To modify the Bitcoin blockchain, all miners must agree on the new rules and what constitutes a valid block on the chain. To change the rules, you must “fork” it to change to indicate that something has changed from the original protocol. These situations are called Bitcoin forking.
Usually, forks are used to add new features or change some blockchain parameters. The forking process results in the blockchain being divided into two distinct blockchains after a certain point in time. Although there have been many forks since the inception of Bitcoin, only a few are viable projects.
Crypto forks can be either soft or hard forks. The main difference is that soft forks are not a fork that results in a new currency and new branches of the blockchain. Soft forks slightly modify the Bitcoin protocol, but the core Bitcoin blockchain remains the same. Soft forks are backwards compatible, which means that the upgraded chain can successfully share and use data from earlier network versions.
However, during a hard fork, the programming code of the Bitcoin blockchain and its mining processes are upgraded. Once a user has updated their software, it rejects transactions from any older version, creating a new branch to the blockchain. Users who keep the older software can still process transactions. This means that transactions are being processed on two separate chains, and two different currencies result from the hard fork.
This is how various digital currencies, similar names to Bitcoin, have been created. These include Bitcoin Cash and Bitcoin Gold.
While not many investors know, anyone who owns Bitcoin, during a hard fork, is entitled to the new cryptocurrency. That’s why some consider that there’s an obvious financial incentive to fork Bitcoin’s blockchain and made some investors sceptical of the necessity of these forks.
Since it can be confusing for casual investors to distinguish between these cryptocurrencies, we’ll be going through the top Bitcoin hard forks.
Bitcoin Forks History
Bitcoin has over 100 forks, but not all projects were further developed, and only a few remain functional today. You can find the complete list of Bitcoin forks on forkdrop.io. We’ll mention the most noteworthy Bitcoin forks here.
Bitcoin XT
Bitcoin XT fork took place on December 27, 2014.
Bitcoin XT is the first known Bitcoin hard fork. Mike Hearn incorporated some of his ideas into the Bitcoin blockchain and launched Bitcoin XT in late 2014. It is said that Hearn is one of the few to have contacted Satoshi Nakamoto via email.
Bitcoin XT was designed to allow 24 transactions per second. The previous version of Bitcoin could only handle seven transactions per second. It proposed to increase the block size from 1 megabyte to 8 megabytes.
Initially, Bitcoin XT was a success. In 2015, it had more than 1,000 nodes running the software. But, just a few short months later, investors lost interest, and the project was abandoned. Bitcoin XT has been removed from the internet, and its website is not functional anymore.
Bitcoin Classic (BXC)
Bitcoin Classic fork took place in early 2016.
Jonathan Toomim launched Bitcoin Classic in early 2016 as some community members wanted to see block sizes increase after Bitcoin XT’s decline.
Bitcoin Classic, like Bitcoin XT, saw a lot of initial interest. In 2016, there were approximately 2,000 nodes in use. The Bitcoin Classic (BXC) fork proposed a smaller block size of 2 MB.
The BXC coin still exists, but it seems that the community has moved on. The website is no longer live.
Bitcoin Unlimited
Bitcoin Unlimited (BU) fork took place on March 11, 2016.
Bitcoin Unlimited has remained a mystery since its initial release in 2016.
Bitcoin Unlimited is unique because it allows miners to choose the size of their blocks. Nodes and miners can limit the number of blocks they accept up to 16 megabytes. The community behind Bitcoin Unlimited believes in market-driven decision making, emergent consensus, and giving their users choices.
Despite some initial interest, Bitcoin Unlimited has not been widely accepted. Only a few nodes are still online.
Bitcoin Cash (BCH)
Bitcoin Cash fork took place on August 1st 2017 (BTC block 478,558).
Pieter Wuille, a Bitcoin Core developer, presented the idea for Segregated Witness (SegWit) in late 2015. SegWit is a project that aims to decrease the size of Bitcoin transactions, thus allowing for more transactions to occur simultaneously. Technically, SegWit is a soft fork.
In response to SegWit, some Bitcoin developers and users decided to initiate a hard fork to avoid the protocol updates it brought about. Bitcoin Cash was the result of this hard fork. It split off from the main blockchain in August 2017, when Bitcoin Cash wallets rejected Bitcoin transactions and blocks.
Bitcoin Cash allows blocks of eight megabytes and does not accept the SegWit protocol.
Bitcoin Cash remains the most successful Bitcoin hard fork, and it is backed by many in the cryptocurrency community. BCH can be traded on popular exchanges (Binance, Coinbase, Huobi, Gate.io).
BitCore (BTX)
BitCore (BTX) fork took place on April 24, 2017.
BitCore is an unspent transaction output (UTXO) fork of Bitcoin, and it was launched in 2017. BitCore used Bitcoin’s source code to create a new blockchain but updated the core to make the blockchain size smaller (which makes the network easier to scale). BitCore uses the MEGABTX consensus algorithm, which is ASIC-resistant.
Because anyone can become a BitCore miner, it is impossible to centralise mining power. BitCore also has a 10 MB Segwit-enabled block that allows it to handle 17.6 billion transactions per annum or 48 million transactions per hour.
The entire crypto community can mine BTX using PoW and Masternodes.
Bitcoin Gold (BTG)
Bitcoin Gold fork took place on October 23rd 2017 (BTC block 491,407).
Bitcoin Gold is a hard fork that occurred shortly after Bitcoin Cash. The creators implemented this hard fork to restore mining functionality using basic graphics processing unit (GPU) because they felt mining had become too specialised.
The Bitcoin Gold hard fork featured a pre-mining of the Bitcoin Gold crypto. Pre-mining is when the development team creates the coin from the start. In this case, the Bitcoin Gold developers pre-mined 100,000 BTG. Developers said that these pre-mined coins will be used to grow the Bitcoin Gold ecosystem and pay developers.
Bitcoin Diamond (BCD)
Bitcoin Diamond (BCD) fork took place on November 24, 2017 (BTC block 495.966).
Bitcoin Diamond is a fork of the original Bitcoin blockchain. Bitcoin Diamond was created only two weeks after the Bitcoin Gold fork.
The BCD’s code allows for 100 transactions per second, increasing the block size to 8 megabytes, thus making it more efficient than Bitcoin. While this is an improvement, considering Bitcoin’s seven transactions per second, other cryptocurrencies have much greater transaction throughput, and that’s why some consider Bitcoin Diamond obsolete.
However, the first major Bitcoin hard fork, Bitcoin Cash, can process 116 transactions per second through its increased block size. Although these cryptocurrencies may not be the same, Bitcoin Cash and Bitcoin Diamond are very similar. Some investors wonder if Bitcoin Diamond was a necessary hard fork.
Bitcoin SV (BSV)
Bitcoin SV hard fork took place on November 15th 2018 (BCH block 556,766). It is a fork from the Bitcoin Cash blockchain.
Bitcoin SV‘s goal is to realise the original vision and design of Bitcoin as described in Satoshi Nakamoto’s whitepaper.
BSV is designed to provide stability and scalability while keeping Bitcoin a peer-to-peer electronic money system. It also aims to become a distributed data network that can support enterprise-level advanced blockchain applications.
It has also removed artificial block sizes limits, re-enabled script commands, and other technical capabilities that had been previously disabled or restricted by protocol developers on the BTC blockchain. The network can process thousands of transactions per second while keeping transaction fees low for micropayments. It also offers advanced capabilities like tokens, smart contracts and other use cases.
The block size of Bitcoin SV can go up to 2Gb and can process over 10,000 transactions per second. BSV reached over 50.000 TPS on the testnet.
BSV is unmatched in its ability to scale on-chain without any restrictions while being closer to the original Bitcoin design than any other blockchain.
Bitcoin Cash ABC (eCash)
Bitcoin Cash ABC fork took place on November 15, 2020 (BCH block 661648).
Bitcoin Cash ABC (BCHA) is a cryptocurrency that was created in 2020 as a result of a hard fork within the Bitcoin Cash blockchain. This split the original chain into two new ones called “Bitcoin Cash ABC” and “Bitcoin Cash Node.”
Amaury Sechet is the leader of the Bitcoin Cash ABC developers. They proposed an update to the Bitcoin Cash network. This update included a controversial new “Coinbase Rule,” requiring 8% of all mined Bitcoin Cash to be distributed to BCH ABC to finance protocol development.
Another group, Bitcoin Cash Node from the Bitcoin Cash community, opposed the upgrade. They removed the so-called “miner tax” from their source code.
In July 2021, Bitcoin Cash ABC (BCHA) was rebranded as eCash (XEC). With this relaunch, the team also announced their plans to integrate the proof-of-stake consensus layer Avalanche, which introduces great improvements to the network.
Three main improvements are:
- Scaling transaction throughput to more than 5,000,000 transactions per second
- Improve the payment experience by reducing transaction finality
- Protocol extension and fork-free upgrades
The eCash (XEC) rebrand also decreases the coin’s decimal from eight to only two.
Beware of Bitcoin Forks Scams
You should also bear in mind that some Bitcoin forks were created as a scam. Bitcoin Platinum, for instance, was created to lower Bitcoin’s value. Other scams, such as the fake Bitcoin Gold wallet, were created to steal your real funds. That’s why it’s crucial to keep your crypto funds safe and don’t trust everyone you talk to over the internet.
At the same time, you should be aware that some developers just want to make quick money. While some Bitcoin forks seem to be similar, the primary reason for their creation is more marketing buzz. Many developers are looking for free coins, and Bitcoin forks have become the new ICOs. The team creates the fork only to sell the coins on crypto exchanges as soon as it starts trading.
To reduce your chances of losing any Bitcoin, you have to move your Bitcoin to a new wallet before claiming any coins.
How to safely claim coins from a fork
Before attempting to claim any Bitcoin fork coins, you should research the new project and the team of developers behind it to establish its legitimacy. They should also provide a clear and accurate roadmap for the project they want to build.
For instance, a Bitcoin fork coin should implement replay protection, to allow the new network to separate from its original.
Depending on the specific Bitcoin fork, you might need to perform certain risk actions such as exposing your Bitcoin wallet private keys, installing specific software or validating your identity on centralised crypto exchanges.
One of the easiest ways to claim Bitcoin fork coins is to use wallets that support them. Note that most wallets don’t support many of the Bitcoin forks simply because the process requires complicated technical developments, which is not feasible for most wallets. This is because most of the Bitcoin forks don’t have a great market value and lack a development team and community.
Bitcoin forks can have various aspects to consider:
- Coin ratio. Depending on the Bitcoin fork, the new coins (forked-coins) can be claimed at a specific ratio (It’s mostly a 1:1 ratio, but it can vary).
- Fork height. The Bitcoin block height at the time that the Bitcoin Fork took place. Bitcoin wallets that received BTC after that date are not eligible for the Bitcoin fork claim.
- Crypto exchange availability. Minor and less successful Bitcoin fork coins will not be supported by a lot of crypto exchanges.
Before attempting to claim any Bitcoin fork coins, you should go through these simple (but effective against theft) steps.
Step 1. Move Bitcoin to a new wallet
For all Bitcoin fork claims and any forks in general, users need to provide the wallet’s private keys in which the Bitcoin was held at the time of the Bitcoin fork. You should never share the keys of an active wallet.
That’s why, for safety reasons, moving the crypto funds to a different crypto wallet should be performed first before revealing the private keys to any third party. By doing this, you eliminate any possibility of having your Bitcoin stolen.
If you still have a Legacy Bitcoin wallet with addresses beginning with 1, claiming these forks can be a great motivation to move your coins to a SegWit account. This will lower your transaction fees and allow you to use Lightning Network.
Step 2. Export private keys
Firstly, you will need to export your private key from the wallet that was used to hold the Bitcoin funds at the time of the fork. Most wallets are able to export a file containing all the addresses and private keys. However, hardware wallets don’t allow private keys export, and for such cases, you need to enter the seed phrase into specific claiming software.
Using the seed phrase, you can also use open-source tools such as BIT39 to find a wallet’s pirate keys.
You can import only private keys that have funds to save time.
Step 3. Check Bitcoin wallet address for available claims
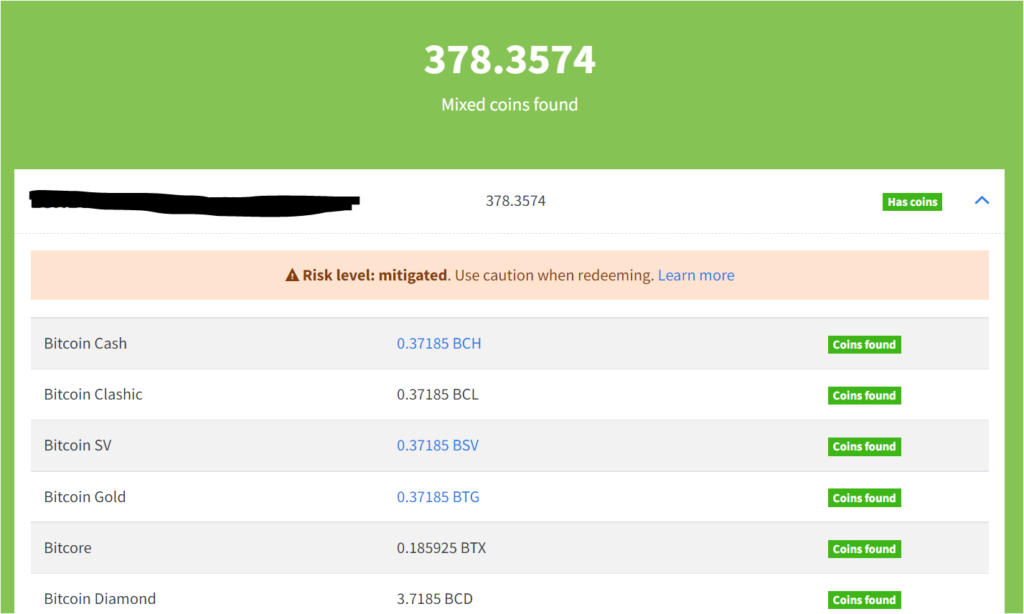
Using your Bitcoin wallet address, you can check if your address is entitled to a Bitcoin fork claim on Findmycoins.ninja.
You should save all the claimable wallets’ addresses and private key combinations.
All valid addresses and private key combinations should be recorded in a spreadsheet or text file that allows you to copy, paste, or replace text. The recording format should include a private key followed by the address.
Each entry should be numbered and the amount of Bitcoin they contain at the time of the first fork. It will be helpful to number each key pair for ordering purposes. It may be useful to note the sizes. You can, for example, use the address with the smaller amount to test the process.
Step 4. Claim the Bitcoin fork coin using a crypto wallet
There are several secure crypto wallets that can help you claim some of the most popular Bitcoin forks, such as:
- Coinomi. Supports Bitcoin Cash (BCH), Bitcoin Gold, Bitcoin SV (BSV). Find the guide on how to claim Bitcoin forks on their support page.
- Exodus. Supports Bitcoin Cash, Bitcoin Gold, and Bitcoin SV.
- BitPie & Bither wallets. These are two distinct mobile app Bitcoin wallets. BitPie is used to claim the coins, and then Bither can be used to sell them. Using the two wallets you can successfully claim Super Bitcoin (SBTC), BTW, BCD, BTF, BTP, BTN, Bitcoin Cash and Bitcoin Gold.
While the BitPie and Bither wallets are the most common solution you can find on the web these days to claim your Bitcoin forks, the wallets do not support BTC fork claiming anymore. We tried this option without any success.
How to use Coinomi for Bitcoin fork claims
Step 1. Install and create a Coinomi wallet
Firstly, make sure you have the latest version of Coinomi on your mobile device. Afterwards, create a new wallet, and make sure to write down its seed phrase to recover your funds later, in case something happens to the mobile device. You will also be asked to set up a password for this specific wallet and device.
Step 2. Select the coins you want to add
Before claiming the Bitcoin forks in the Coinomi wallet, you need to select the specific coins as balances in your Coinomi wallet.
Click on the bottom-right plus sign and select Add coins. Select the Bitcoin forks you will be adding (e.g. Bitcoin Cash (BCH), Bitcoin Gold (BTG), BitcoinSV (BSV)).
Step 3. Claim Bitcoin fork coins
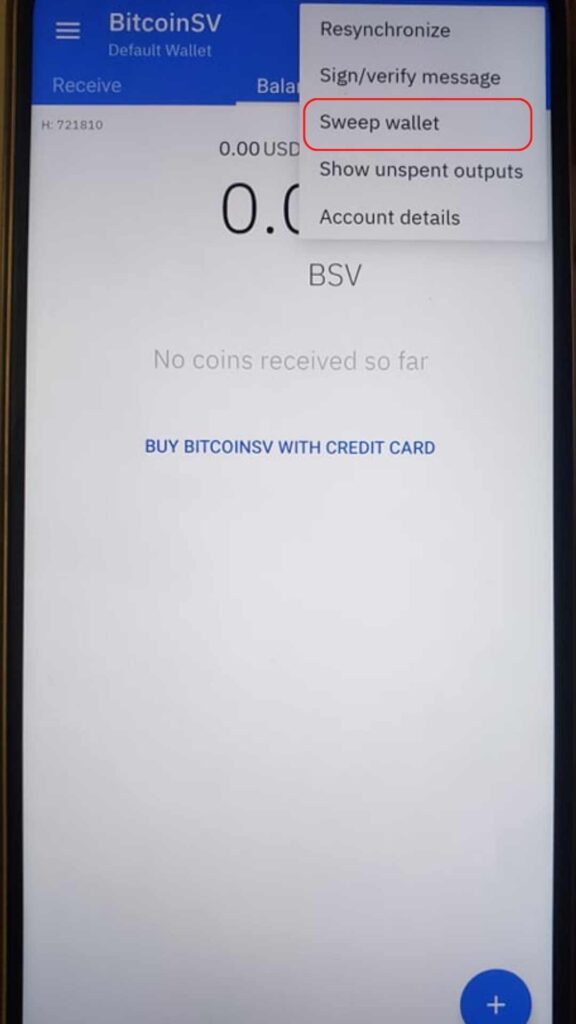
Select the coin you want to claim the Bitcoin fork for, and within that specific wallet, click on the top menu > Sweep wallet.
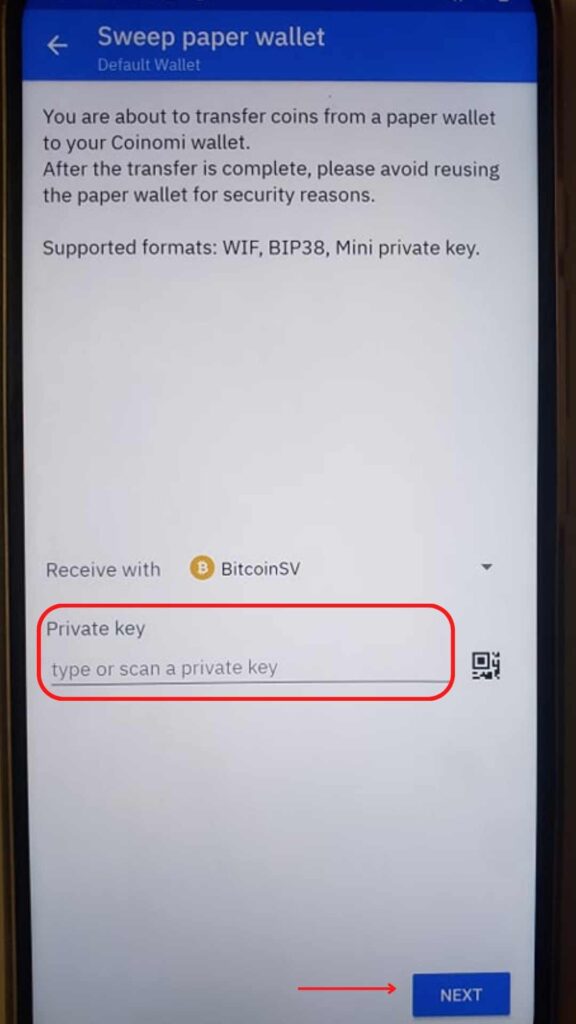
You will have to paste or scan the wallet’s private key that had the Bitcoin at the time of the fork.
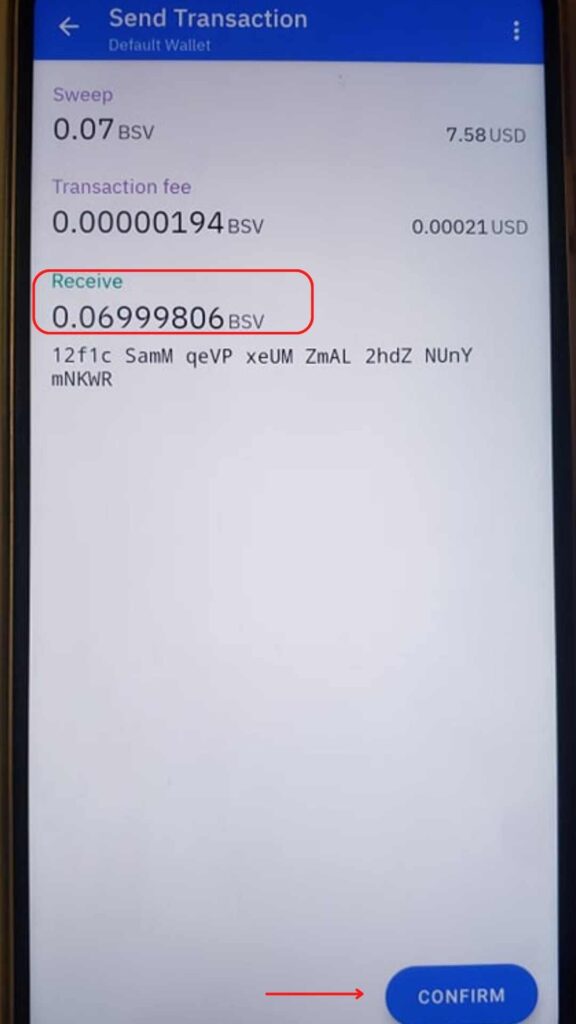
After you get all the transaction details (The amount of Bitcoin fork coins you will receive, the value in USD, the transaction fee), review all the details and tap Confirm.
You will then see the updated balance for the Bitcoin fork coins.
Repeat this step for every address with a balance of the forked coin.
How to claim Bitcoin forks using Ymgve’s Fork Claimer
More advanced crypto users that do not want to rely on a specific Bitcoin wallet, can use Ymgve’s script to claim the most Bitcoin forks. This method will require some technical knowledge on the user’s side because you will need to run a Phyton script.
The Ymgve is open-source. It is available on GitHub, along with all the information about how to use the script. Ymgve supports standard P2PKH and Segwit P2SH-P2WPKH addresses.
Using the Ymgve fork claimer script is recommended if you want to claim most forks, although it’s riskier and mistyping any of the commands can result in a loss of funds.
How do Bitcoin hard forks influence Bitcoin holders?
By the end of 2021, there have been over 100 Bitcoin hard forks, and investors expect to see more soft and hard forks in the years to come. However, out of all the hard forks to date, only a few are still operational.
Long time investors are entitled to claim all of these Bitcoin hard forks. Luckily there are ways to do so, using the wallets described in this article. However, as of the beginning of 2022, no Bitcoin fork has raised more in popularity than the original Bitcoin.